Page 187 - 2021_03-Haematologica-web
P. 187
Porcine model of hemophilia B
A
B
D
C
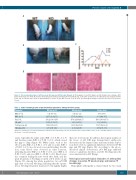
Figure 3. The bleeding phenotype of pF9 knockout (KO) pigs and hF9 knockin (KI) pigs. (A) Photographs of a pF9 KO piglet, an hF9 KI piglet and a wild-type (WT) piglet twenty days after birth. (B) Pictures illustrating joint swelling and limping in hemophilia B pigs. (C) Relative spontaneous bleeding frequency in pigs from birth to the age of 8 weeks with a peak at approximately 5-6 weeks of age (WT, n=2; KO, n=5; KI, n=3). (D) Histological changes in porcine liver tissues. Scale bars: 50 mm.
Table 1. Some hematologic and serum biochemical parameters among the three groups.
Parameter
RBC, x1012/L
WBC, x109/L Plt, x109/L
Hb, g/dL
Total protein, g/L
Albumin, g/dL
WT pigs (n=4)
6.15 (4.8-7.5)
24.55 (20.8-27.7)
237.22 (196.6-276)
13.23 (10.7-16.7)
58.48 (54.9-63.5)
2.90 (2.65-3.21)
KO pigs (n=4)
3.55 (2.1-5.2)
37.95 (32.1-44.9)
255.8 (224.4-282.7)
9.23 (6.9-11.6)
38.95 (22.6-56.2)
2.02 (1.2-2.85)
KI pigs (n=3)
4.67 (3.8-6)
30.5 (24.4-35.5)
254.9 (246.9-265.6)
10.6 (9.2-12.1)
53.87 (42.6-60.2)
2.69 (2.03-3.06)
Numbers in parentheses represent the minimum to maximum values.WT: wild-type; KO: knockout; KI: knockin; n: number; RBC: red blood cell count;WBC: white blood cell count; Plt:platelet count;Hb:hemoglobin.
joints, especially the ankle joints (KO: 4 of 5; KI: 2 of 3) and the knee joints (KO: 4 of 5; KI: 0 of 3), which caused the pigs to limp (Figure 3B). Other joints, such as the elbow joints (KO: 2 of 5; KI: 1 of 3) and toe joints (KO: 1 of 5; KI: 1 of 3), also showed occasional bleeding. In addi- tion, some bleeds were observed in other locations, including muscles (KO: 2 of 5; KI: 0 of 3), nose (KO: 2 of 5;KI:0of3),andeyes(KO:1of5;KI:0of3).Bleedswere less common during the first week after birth, and the peak frequency of bleeding occurred at 5-6 weeks of age (Figure 3C). Among the whole population, two pF9 KO pigs died of visceral bleeding, indicating that the sponta- neous bleeding frequency may have been slightly higher
than our observations. In addition, histological analysis of the livers of pF9 KO pigs demonstrated erythrocyte destruction in the hepatic sinus and hemosiderin deposi- tion; there were no significant differences between hF9 KI pigs and WT pigs (Figure 3D). According to the above- described clinical observations, pF9 KO pigs exhibited serious coagulation disorders, and the bleeding episodes were ameliorated in hF9 KI pigs.
Histological and radiological evaluation of arthropathic changes in porcine F9 knockout pigs and human F9 knockin pigs
Hemophilic arthropathy is characterized by two main
haematologica | 2021; 106(3)
833