Page 189 - 2021_03-Haematologica-web
P. 189
Porcine model of hemophilia B
ovitis were found in hF9 KI pigs (Figure 4C). Cartilage destruction occurred in both pF9 KO pigs and hF9 KI pigs (Figure 4D). Apart from these findings, coagulated blood was present in the joint cavity of pF9 KO pigs, creating a damaged microenvironment around the joint surfaces (Figure 4E and F).
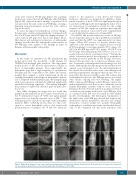
To assess the impact of hemarthrosis on bone changes, the pigs were evaluated radiographically. Compared with those of WT pigs and hF9 KI pigs, the epiphyseal plates of some joints in pF9 pigs were fused early (Figure 5A-C). Histological and radiological evaluation of arthropathic changes revealed that the arthropathic characteristics in pF9 KO pigs were similar to the findings in joints of humans with hemophilic arthropathy.
Discussion
In this study, we generated an HB translational pig model and tested the possibility of HB therapy by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene insertion. This large mam- malian model of HB showed characteristics similar to those of hemophilic patients. Most importantly, the hemophilic pigs had a high frequency of spontaneous bleeding episodes (especially in the ankles and knees), making these animals a useful translational model for studying hemophilic arthropathy in hemophiliac individ- uals. Compared with hemophiliac pigs, the transgenic pigs with a gene insertion of human F9 exhibited significantly ameliorated bleeding symptoms. This finding highlights the potential to replace the defective gene by gene inser- tion in situ.
First, while designing the target sites, we found that multiple point mutations in the F9 gene were present in the 5’ untranslated region (5’ UTR) and signal peptide region based on clinically reported cases of HB.30-33 The resulting missense mutations in people with hemophilia indicates FIX:C or FIX:Ag are less than 1%; this corre- sponds to severe hemophilia, such as that found with point mutations occurring at -55, +8 and +19, which are
related to the initiation codon (Factor IX Variant Database). Therefore, we designed two sgRNAs to target partial sequences of the 5’ UTR and signal peptide region to produce an HB pig model. In designing the donor vector for homologous recombination, except for the coding sequence of hF9, the regulatory sequences preceding the endogenous initiation codon of pF9 were complemented to avoid affecting the expression of human FIX.
The mRNA and protein expression results in HB pigs showed that the expression of porcine FIX was extremely weak and that the APTT was approximately four times longer. When FIX activity in porcine plasma was expressed as the percentage of coagulation factor activity in WT pig plasma, it was approximately 5.5% (range: 4.5- 6.2%) in pF9 KO pigs and 13.5% (range: 12.3-15.0%) in hF9 KI pigs. Increasing plasma FIX levels as low as 1% results in the restoration of clotting activity.34-36 During the whole observation period, the frequency of spontaneous bleeding decreased markedly in hF9 KI pigs. However, there is still some way to go to achieve our ultimate objec- tive. For patients, achieving relief from bleeding is not suf- ficient. Arthropathy develops progressively and this devel- opment is not interrupted once the initial hemarthrosis has started. In our models, there were some differences in paraclinical parameters among the three groups. We sus- pected that the decreases in RBC counts, Hb, total protein and albumin levels in two pF9 KO pigs may be associated with chronic ongoing non-overt bleeding. The higher WBC counts in pF9 KO pigs and hF9 KI pigs could not be readily explained because they are not commonly seen in human hemophilic patients without acute infections. During an 8-week observation period, spontaneous bleeds occurred very frequently in the joints of pF9 KO pigs. This is a unique feature that was not found in other animal models of hemophilia. The histological examination of the ankle joints of pF9 KO pigs showed that without any intervention chronic proliferative synovitis and cartilage destruction occurred within two months. Hemophilic arthropathy is a multifactorial event, and detailed knowl- edge of the sequential cell and tissue responses after
ABC
Figure 5. Radiological changes in some joints of pF9 knockout (KO) pigs and hF9 knockin (KI) pigs. (A) Elbow joints, (B) shoulder joints, (C) ankle joints. Arrows indi- cate the epiphyseal plates that were fused in hemophilic pigs. WT: wild-type; L: left; R: right.
haematologica | 2021; 106(3)
835