Page 176 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 176
J. Tong et al.
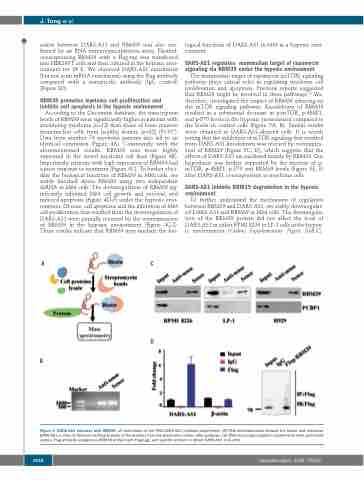
action between DARS-AS1 and RBM39 was also con- firmed by an RNA immunoprecipitation assay. Plasmid- overexpressing RBM39 with a Flag-tag was transferred into HEK293T cells and then cultured in the hypoxic envi- ronment for 24 h. We observed DARS-AS1 enrichment (but not actin mRNA enrichment) using the Flag antibody compared with a nonspecific antibody (IgG control) (Figure 3D).
RBM39 promotes myeloma cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis in the hypoxic environment
According to the Oncomine database, the transcription levels of RBM39 were significantly higher in patients with smoldering myeloma (n=12) than those of bone marrow mononuclear cells from healthy donors (n=22) (P<10-4). Data from another 74 myeloma patients also led to an identical conclusion (Figure 4A). Consistently with the aforementioned results, RBM39 was more highly expressed in the tested myeloma cell lines (Figure 4B). Importantly, patients with high expression of RBM39 had a poor response to treatment (Figure 4C). To further eluci- date the biological functions of RBM39 in MM cells, we stably knocked down RBM39 using two independent shRNA in MM cells. The downregulation of RBM39 sig- nificantly inhibited MM cell growth and survival, and induced apoptosis (Figure 4D-F) under the hypoxic envi- ronment. Of note, cell apoptosis and the inhibition of MM cell proliferation that resulted from the downregulation of DARS-AS1 were partially reversed by the overexpression of RBM39 in the hypoxic environment (Figure 4G-I). These results indicate that RBM39 may mediate the bio-
AC
D
B
Figure 3. DARS-AS1 interacts with RBM39. (A) Schematic of the RNA DARS-AS1 pulldown experiment. (B) RNA electrophoresis showed the sense and antisense DARS-AS1 in vitro.(C) Western blotting analysis of the proteins from the proteomics screen after pulldown. (D) RNA immunoprecipitation experiments were performed using a Flag antibody (exogenous RBM39 protein with Flag-tag), and specific primers to detect DARS-AS1 or β-actin.
logical functions of DARS-AS1 in MM in a hypoxic envi- ronment.
DARS-AS1 regulates mammalian target of rapamycin signaling via RBM39 under the hypoxic environment
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway plays critical roles in regulating myeloma cell proliferation and apoptosis. Previous reports suggested that RBM39 might be involved in these pathways.16 We, therefore, investigated the impact of RBM39 silencing on the mTOR signaling pathway. Knockdown of RBM39 resulted in a substantial decrease in p-mTOR, p-4EBP1, and p-P70 levels in the hypoxic environment compared to the levels in control cells (Figure 5A, B). Similar results were obtained in DARS-AS1-silenced cells. It is worth noting that the inhibition of mTOR signaling that resulted from DARS-AS1 knockdown was rescued by overexpres- sion of RBM39 (Figure 5C, D), which suggests that the effects of DARS-AS1 are mediated mainly by RBM39. Our hypothesis was further supported by the increase of p- mTOR, p-4EBP1, p-P70 and RBM39 levels (Figure 5E, F) after DARS-AS1 overexpression in myeloma cells.
DARS-AS1 inhibits RBM39 degradation in the hypoxic environment
To further understand the mechanism of regulation between RBM39 and DARS-AS1, we stably downregulat- ed DARS-AS1 and RBM39 in MM cells. The downregula- tion of the RBM39 protein did not affect the level of DARS-AS1 in either RPMI 8226 or LP-1 cells in the hypox- ic environment (Online Supplementary Figure S5B,C).
1634
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)