Page 174 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 174
J. Tong et al.
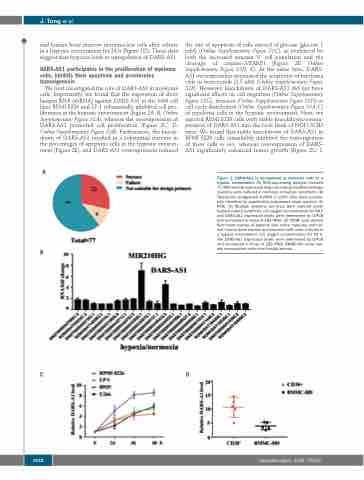
mal human bone marrow mononuclear cells after culture in a hypoxic environment for 24 h (Figure 1D). These data suggest that hypoxia leads to upregulation of DARS-AS1.
DARS-AS1 participates in the proliferation of myeloma cells, inhibits their apoptosis and accelerates tumorigenesis
We next investigated the role of DARS-AS1 in myeloma cells. Importantly, we found that the expression of short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against DARS-AS1 in the MM cell lines RPMI 8226 and LP-1 substantially inhibited cell pro- liferation in the hypoxic environment (Figure 2A, B, Online Supplementary Figure S2A), whereas the overexpression of DARS-AS1 promoted cell proliferation (Figure 2C, D, Online Supplementary Figure S2B). Furthermore, the knock- down of DARS-AS1 resulted in a substantial increase in the percentages of apoptotic cells in the hypoxic environ- ment (Figure 2E), and DARS-AS1 overexpression reduced
A
the rate of apoptosis of cells starved of glucose (glucose 1 mM) (Online Supplementary Figure S2C), as evidenced by both the increased annexin V+ cell population and the cleavage of caspase-3/PARP1 (Figure 2F, Online Supplementary Figure S2D, E). At the same time, DARS- AS1 overexpression attenuated the sensitivity of myeloma cells to bortezomib (2.5 nM) (Online Supplementary Figure S2F). However, knockdown of DARS-AS1 did not have significant effects on cell migration (Online Supplementary Figure S2G), invasion (Online Supplementary Figure S2H) or cell-cycle distribution (Online Supplementary Figure S3A-C) of myeloma cells in the hypoxic environment. Next, we injected RPMI 8226 cells with stable knockdown/overex- pression of DARS-AS1 into the back flank of NOD-SCID mice. We found that stable knockdown of DARS-AS1 in RPMI 8226 cells remarkably inhibited the tumorigenesis of these cells in vivo, whereas overexpression of DARS- AS1 significantly enhanced tumor growth (Figure 2G, I,
Figure 1. DARS-AS1 is upregulated in myeloma cells in a hypoxic environment. (A) RNA-sequencing analysis revealed 77 differentially expressed long non-coding (lnc)RNA between myeloma cells cultured in normoxic or hypoxic conditions. (B) Twenty-two upregulated lncRNA in U266 cells were success- fully identified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Q- PCR). (C) Multiple myeloma cell lines were cultured under hypoxic culture conditions (1% oxygen concentration) for 48 h and DARS-AS1 expression levels were determined by Q-PCR and normalized to those of 18S rRNA. (D) CD38+ cells derived from bone marrow of patients with active myeloma and nor- mal human bone marrow mononuclear cells were cultured in a hypoxic environment (1% oxygen concentration) for 24 h. The DARS-AS1 expression levels were determined by Q-PCR and normalized to those of 18S rRNA. BMMC-HD: bone mar- row mononuclear cells from healthy donors.
B
CD
1632
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)