Page 220 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 220
A. Mikulasova et al.
Lastly, deletions at 8q24 centromeric of MYC are pres- ent in 2.9% (36 of 1,249) of samples (Figure 5 and Online Supplementary Figures S7 and S8), and most frequently result in contraction of the region bringing NSMCE2 into close proximity of MYC (Figure 7C). This interstitial dele- tion results in TAD disruption, bringing the super- enhancer at NSMCE2, present in the cell lines KMS11 and MM.1S, into the same TAD as MYC, resulting in a fused TAD and overexpression of MYC.
8q24 translocations result in increased expression of MYC and PVT1
The biological consequence of rearrangements at 8q24 is thought to be increased expression of MYC, so we examined the available CoMMpass study RNA-sequenc- ing data (Figure 3) and a set of microarray data (Online Supplementary Figure S6), and categorized samples by type and location of breakpoints. In addition to MYC, we examined the expression of other genes in the regions, but only found significant increases in MYC and the non-cod- ing RNA, PVT1 (Figure 3A-F), which were associated with particular types of rearrangements. Expression level of these two genes showed a significant but weak correlation (r=0.4, P<0.001).
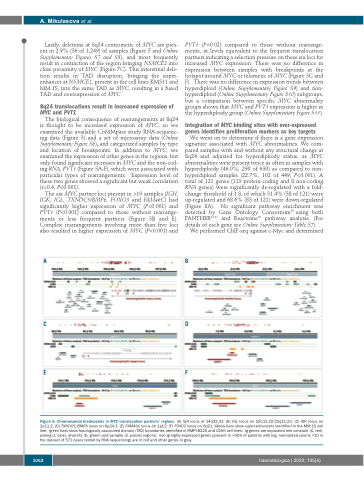
The six MYC partner loci present in >10 samples (IGH, IGK, IGL, TXNDC5/BMP6, FOXO3 and FAM46C) had significantly higher expression of MYC (P<0.001) and PVT1 (P<0.001) compared to those without rearrange- ments or less frequent partners (Figure 3B and E). Complex rearrangements involving more than five loci also resulted in higher expression of MYC (P<0.001) and
PVT1 (P=0.02) compared to those without rearrange- ments, at levels equivalent to the frequent translocation partners indicating a selection pressure on these six loci for increased MYC expression. There was no difference in expression between samples with breakpoints at the hotspot around MYC or telomeric of MYC (Figure 3C and F). There was no difference in expression trends between hyperdiploid (Online Supplementary Figure S9) and non- hyperdiploid (Online Supplementary Figure S10) subgroups, but a comparison between specific MYC abnormality groups shows that MYC and PVT1 expression is higher in the hyperdiploidy group (Online Supplementary Figure S11).
Integration of MYC binding sites with over-expressed genes identifies proliferation markers as key targets
We went on to determine if there is a gene expression signature associated with MYC abnormalities. We com- pared samples with and without any structural change at 8q24 and adjusted for hyperdiploidy status, as MYC abnormalities were present twice as often in samples with hyperdiploidy (46.0%, 290 of 630) as compared to non- hyperdiploid samples (22.7%, 102 of 449; P<0.001). A total of 121 genes (113 protein-coding and 8 non-coding RNA genes) were significantly de-regulated with a fold- change threshold of 1.8, of which 31.4% (38 of 121) were up-regulated and 68.6% (83 of 121) were down-regulated (Figure 8A). No significant pathway enrichment was detected by Gene Ontology Consortium35 using both PANTHER36,37 and Reactome38 pathway analysis. (For details of each gene see Online Supplementary Table S7).
We performed ChIP-seq against c-Myc and determined
AB
CD
EF
Figure 6. Chromosomal breakpoints in MYC translocation partners’ regions. (A) IGH locus at 14q32.33. (B) IGL locus on 22q11.22-22q11.23. (C) IGK locus on 2p11.2. (D) TXNDC5/BMP6 locus on 6p24.3. (E) FAM46C locus on 1p12. (F) FOXO3 locus on 6q21. Yellow bars show super-enhancers identified in the MM.1S cell line; green bars show topologically associated domain (TAD) boundaries identified in RMPI-8226 and U266 cell lines. Ig genes are separated into constant (C, red), joining (J, blue), diversity (D, green) and variable (V, purple) regions; non-Ig highly-expressed genes (present in >95% of patients with log2 normalized counts >10 in the dataset of 571 cases tested by RNA sequencing) are in red and other genes in gray.
1062
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)