Page 205 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 205
HIF-1α in TP53-disrupted CLL cells
A
BCD
EF
G
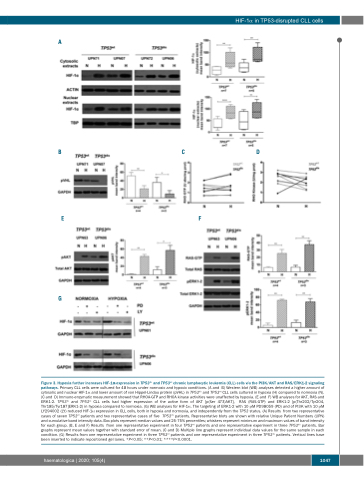
Figure 3. Hypoxia further increases HIF-1α expression in TP53dis and TP53wt chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells via the PI3K/AKT and RAS/ERK1-2 signaling pathways. Primary CLL cells were cultured for 48 hours under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. (A and B) Western blot (WB) analyses detected a higher amount of cytosolic and nuclear HIF-1α and lower amount of von Hippel-Lindau protein (pVHL) in TP53dis and TP53wt CLL cells cultured in hypoxia (H) compared to normoxia (N). (C and D) Immuno-enzymatic measurement showed that RHOA-GTP and RHOA kinase activities were unaffected by hypoxia. (E and F) WB analyses for AKT, RAS and ERK1-2. TP53dis and TP53wt CLL cells had higher expression of the active form of AKT [p(Ser 473)AKT], RAS (RAS-GTP) and ERK1-2 [p(Thr202/Tyr204, Thr185/Tyr187]ERK1-2) in hypoxia compared to normoxia. (G) WB analyses for HIF-1α. The targeting of ERK1-2 with 10 μM PD98059 (PD) and of PI3K with 10 μM LY294002 (LY) reduced HIF-1α expression in CLL cells, both in hypoxia and normoxia, and independently from the TP53 status. (A) Results from two representative cases of seven TP53wt patients and two representative cases of five TP53dis patients. Representative blots are shown with relative Unique Patient Numbers (UPN) and cumulative band intensity data. Box plots represent median values and 25-75% percentiles; whiskers represent minimum and maximum values of band intensity for each group. (B, E and F) Results from one representative experiment in four TP53wt patients and one representative experiment in three TP53dis patients. Bar graphs represent mean values together with standard error of mean. (C and D) Multiple line graphs represent individual data values for the same sample in each condition. (G) Results from one representative experiment in three TP53wt patients and one representative experiment in three TP53dis patients. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate repositioned gel lanes. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ****P<0.0001.
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
1047