Page 180 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 180
I. Cortegano et al.
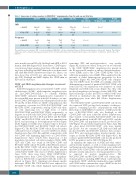
Table 1. Expression of surface receptors in CD45-CD41++ megakaryocytes from the yolk sac and fetal liver.
MFI
Frequency
c-Kit-APC
CD42c-FITC
E10.5 YS
246±35 (3)
402±11
(8)
60±11 (4)
90±1
(8)
E11.5 YS
188±10 (12)
474±10
(10)
63±2 (6)
95±1
(8)
E10.5 FL
281±10 (3)
326±9
(7)
75±7 (5)
82±2
(8)
E11.5 FL
273± 14 (12)
383±12
(8)
77±4 (6)
90±1
(8)
P value E11.5 YS/FL
P<0.001 P<0.001
P<0.01 P<0.01
P value
YS E10.5/E11.5
P<0.05 P<0.001
P<0.01
P value
FL E10.5/E11.5
P<0.01
P<0.01
c-Kit-APC
CD42c-FITC
The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of electronically gated CD45-CD41++ cells was determined.Values are the mean ± standard error of mean and (number).The statistical significances were calculated using unpaired and paired t tests (the latter when values were obtained from the same pools of embryos). E: embryonic day;YS: yolk sac; FL: fetal liver.
were much lower in LSK cells, PreMegE and MKP at E11.5 than in adult BM (Figure 3E-F). In neonates, CD45 expres- sion increased in progenitors from liver, although remain- ing lower in PreMeg and MKP than in those from neonatal and adult BM (Online Supplementary Figure S1). Hence, our data show that at E11.5, not only megakaryocytes, but also LSK, PreMegE and MKP display less CD45 than at PD3 and in adult mice.
CD45+ and CD45- megakaryocyte lineages are present at E11.5
Adult BM megakaryocytes are Lin-CD41++CD45+ acetyl- cholinesterase (AChE)+, while immature megakaryocytes are Lin-CD45+CD41+AChE-.34 To identify whether CD41+CD45+ immature megakaryocytes equivalent to those from BM were present in the E11.5 embryo, we ana- lyzed CD41/CD45 expression in cell preparations from the YS and FL. At E11.5 there are CD45+ cell populations that are negative or positive for CD41 (R1/CD41-CD45++ and R2/CD41+CD45+, respectively). Among CD45- cells there are cells expressing low or high levels of CD41 (R3/CD41+CD45- and R4/CD41++CD45-, respectively), or negative for it (DN cells). R2/CD41+CD45+ cells were high- ly prominent in the YS at E9.5 and E10.5, and R1/CD41- CD45++ and R3/CD41+CD45- cells, the first apparent from E10.5, and increasing as development proceeded (Figure 4A-B). Signals for AChE were obtained only for the puri- fied R2/CD41+CD45+ and R4/CD41++CD45- cell subsets (Figure 4C). The R2/CD41+CD45+ cells in FL can be further subdivided based on higher or lower CD45 level (Online Supplementary Figure S2C; R2a and R2b, respectively), with few CD45+ cells displaying high levels of CD41 (Online Supplementary Figure S2C,D; R2c). Expression of the megakaryocyte-related cell surface markers CD42c, MPL, CD9 and CD61 was found in R4/CD41++CD45- and R3/CD41+CD45- cells in YS and FL at E10.5/E11.5, and also in the R2c/CD41++CD45+ cell subset in FL (Figure 4D and Online Supplementary Figures S2 and S3). Since the number of R2c/CD41++CD45+ cells was low (Online Supplementary Figure S2D), there were fewer CD41++CD45+CD42c+ megakaryocytes than CD41++CD45-CD42c+ megakary- ocytes at E10.5-E11.5, in agreement with the results dis- played in Figure 3B,C. Megakaryocyte-lineage-specific transcripts NF-E2, PF4, VWF and Fli1 were expressed by R4/CD41++CD45- cells, which displayed myeloid-specific
transcripts (PU1 and myeloperoxidase) very weakly (Figure 4E, and data not shown). From now on we will refer to the CD41++CD45-CD42c+ megakaryocytes present in the R4 region in FL samples as embryo-derived megakary- ocytes (EMK), and to the CD41++CD45+CD42c+ cells as adult-type megakaryocytes (AMK). When analyzed for the presence of earlier hematopoietic progenitors by flow cytometry (Figure 4F), R4/CD41++CD45- cells comprise only few MKP besides the EMK. Accordingly, when the differentiation potential of purified R4/CD41++CD45- cells from E11.5 FL cell suspensions was analyzed on clonal MegaCult and MethoCult assays (Figure 4G), they only produced megakaryocyte lineage colonies (MK-CFU), and myeloid lineage colonies (M-CFU) in which P-MK were detected as individual cells, like CD45+CD41++CD42c+ megakaryocytes from adult BM (Online Supplementary Figure S4C).
The R2/CD41+CD45+ and R3/CD41+CD45- cell subsets also expressed VWF, yet they had a mixture of other pro- genitors, containing Lin-c-Kit++ subpopulations with the phenotype of GMP, MKP, low numbers of CMP, and in the case of R3/CD41+CD45- cells, also PreMegE, as did CD41+CD45+ cells from adult BM (Online Supplementary Figure S4A,B). Consequently, R2/CD41+CD45+ cells from FL and BM produced both MK-CFU and M-CFU, and the R3/CD41+CD45- cell population from FL produced E/M- CFU (Figure 4G and Online Supplementary Figure S4C). On the other hand, R1/CD41-CD45++ cells were mainly Lin+CD11b+, but also contained CLP, CMP and GMP, and produced M-CFU and E/M-CFU. Likewise they accumu- lated PU1 and myeloperoxidase myeloid-specific tran- scripts, as did the R2/CD41+CD45+ cells (Figure 4E-G). By contrast, purified DN/CD41-CD45- cells mostly produced E-CFU progenitors and no MK-CFU (Figure 4G).
In summary, the expression of AChE and other surface and molecular markers, as well as clonal megakaryocyte and hematopoietic lineage differentiation assays indicated that R4/CD41++CD45-CD42c+ cells are EMK with low pro- liferative activity and prone to develop proplatelets in vitro, as expected for mature megakaryocytes. The R2/CD41+CD45+ and R3/CD41+CD45- cells contain oligo- clonal progenitors including MKP, which could represent, respectively, CD45+ adult-like intermediate stages (iAMK) and CD45- embryo intermediate stages (iEMK) in the dif- ferentiation of the megakaryocyte lineage.
1858
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)