Page 155 - 2019_09-HaematologicaMondo-web
P. 155
Characterizing energy metabolism of CLL
AB
C
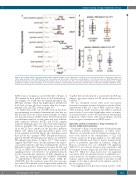
Figure 2. Associations between genetic variants and bioenergetic features. (A) The distribution of P-values of the associations between each genetic variant and each energy metabolic feature (ANOVA test). Gray: associations that did not pass a threshold corresponding to a 5% false discovery rate (FDR) (Benjamini and Hochberg method); red: associations with higher bioenergetic values in mutated cases; blue: associations with lower bioenergetic values in mutated cases (or high- programmed subtype). (B and C) Examples of associations, visualized in beeswarm plots. (B) Glycolysis and IGHV status. (C) Glycolysis and DNA methylation cluster.
IGHV status is strongly associated with three subtypes of CLL defined by their global levels of CpG methylation.14 Accordingly, we found that the high-programmed CLL (HP-CLL) subtype, which has higher global methylation level, had a lower glycolysis activity than the low-pro- grammed CLL (LP-CLL) subtype (Figure 2C).
To further dissect the role of IGHV status in metabolic reprogramming, we analyzed transcriptome data that we had measured for 120 of these patient samples (of which 111 had annotation for IGHV status). We performed gene set enrichment analysis on the genes that were differen- tially expressed between M-CLL and U-CLL samples using the Hallmark gene sets from Molecular Signature Database (MsigDB).15 We found that genes down-regulat- ed in M-CLL were enriched in the glycolysis pathway (Figure 3A). Thirty-four glycolysis-related genes were down-regulated in M-CLL (Figure 3B), including several that encode key enzymes PFKP (Phosphofructokinase, platelet), PGAM1 (Phosphoglycerate Mutase 1), and PGK1 (Phosphoglycerate kinase 1) (Figure 3C).16-18 This analysis suggests that IGHV status directly influences the expres- sion of genes related to glycolysis resulting in the observed difference in glycolytic parameters between M-CLL and U-CLL. As IGHV status reflects the B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling activity,19 we referred to two published datasets for the transcriptomic signatures of BCR stimulation in CLL, either by anti-IgM antibody20 (GEO ID: GSE49695) or unmethylated bacterial DNA (CpG) (GEO ID: GSE30105). In both conditions, genes that were up-regu- lated after BCR stimulation were significantly enriched in the glycolysis pathway (Online Supplementary Figure S3).
Together these results indicate a causal link from BCR sig- naling to glycolysis activity in CLL, in line with previous evidence.21,22
We also identified several other novel associations between bioenergetic features and genetic variants (Online Supplementary Figure S4). Gain of 8q24, deletion of 8p12, ATM mutation, EGR2 mutation and MED12 mutation were found to be associated with higher values of respira- tion-related features such as ATP production and maximal respiration, while tumors with chromothripsis showed lower oxygen consumption rate (OCR) values.
Glycolytic activity contributes to drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Sensitivity to drugs is an informative cellular phenotype that reflects pathway dependencies of tumor cells.10 Therefore, we asked how the 11 intrinsic bioenergetic fea- tures were related to the vulnerabilities of CLL cells towards a panel of 63 drugs applied ex vivo. This panel comprised clinically used drugs as well as small molecule probes of pathways important in leukemia. Using the Pearson correlation test, we identified 118 significant (FDR=10%) associations between drug sensitivities and bioenergetic features (Figure 4A and Online Supplementary Figure S5). Thirty-two drugs had at least one significant association with a bioenergetic feature. A significant asso- ciation between a bioenergetic feature and an ex vivo drug response indicates that the sensitivity or resistance of CLL samples to the drug is affected by the intrinsic activity of the bioenergetic feature.
At an aggregate level, glycolysis-related features of the
haematologica | 2019; 104(9)
1833