Page 282 - 2022_01-Haematologica-web
P. 282
A. Astori et al.
AC
B
D
EF
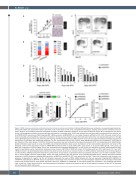
Figure 3. RINF silencing accelerates erythroid maturation of human primary erythroblasts. Erythroid differentiation was monitored in six separate experiments per- formed with CD34+ cells isolated from either cord blood (n=3) or adult bone marrow (n=3), using different techniques. Despite donor-to-donor variability in the mat- uration kinetics, we consistently observed accelerated maturation for RINF knockdown conditions. Of note, data presented in Figure 3B, C correspond to two distinct donors. (A) Hemoglobin production of primary cells was estimated by a benzidine assay. CD34+ cells isolated from cord blood were transduced with the lentiviral vec- tor pTRIPDU3/GFP expressing a shRNA targeting RINF mRNA expression (shRNA/RINF) or a non-target sequence (shRNA/Control). GFP+ cells were sorted by fluo- rescent activated cell sorting (FACS) 2 days after transduction. The black arrow at day 6 indicates the kinetic point selected for one representative picture in the right panel. (B) Morphological analysis was performed after staining with May-Grünwald-Giemsa (MGG). A Fisher exact test was applied to determine whether the observed acceleration of maturation was statistically significant. For this, enumerated erythroid cells (n=454) were segregated into either early (Progenitors, ProE, Baso) or late (Polychro, Ortho, Retic) groups. P<0.0001. (C) Erythroid maturation was also monitored by flow cytometry using anti-CD71 and anti-glycophorin-A (GPA/CD235a) labeled antibodies (upper panel) or using anti-CD49d and anti-Band3 antibodies (lower panel). Scattergrams of two representative experiments are shown (n=6), indicating a more mature population of cells for shRNA-RINF conditions either at day 6 of EPO (GPA+, upper panel), or at day 10 of EPO (Band3+, lower panel). (D) RINF loss of expression in human CD34+ cells is also associated with accelerated downregulation of cKIT and PU.1. A histogram of relative mRNA expression deter- mined by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) for RINF (left panel), cKIT (middle panel) and PU.1 (right panel). PU.1 and c-KIT mRNA are known to be downregulated upon erythroid maturation and are used here as molecular markers. In RINF knockdown cells (black bars), the downregulation of c-KIT and PU.1 mRNA preceded that observed in control cells by at least 3 days, in agreement with an accelerated maturation. (E, F) In order to validate our data with a second shRNA sequence targeting RINF, CD34+ cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector pLKO-Tet-ON/shRNA vector, allowing doxycycline-inducible expression of shRNA sequences targeting RINF expression (shRINF#3 or shRINF#4). GFP+ cells were sorted by FACS 2 days after transduction and cultured in the presence of doxycycline 0.2 mg/mL. (E) The left histogram represents the levels of RINF mRNA obtained with the two sequences targeting RINF (shRINF#3 or shRINF#4) and detected by qRT-PCR. Values are expressed in percentage of the shControl condition. The right histogram represents the percentages of benzidine positive cells obtained with the three shRNA sequences (shControl, shRINF#3, or shRINF#4). (F) Cell culture growth was monitored in one additional experiment (here, a pool from 2 adult donors) and the cumulative population doublings is indicated (left panel) as well as the fold expansion between D0 and D17 of treatment with erythropoietin (EPO) (right panel).
274
haematologica | 2022; 107(1)