Page 97 - 2021_05-Haematologica-web
P. 97
Zebrafish Hax1-associated neutropenia
rable with that in the control group (Figure 6E), indicating that g-csfa is sufficient to reverse the reduced neutrophil numbers in hax1 morphants.
Discussion
In this study, we show that hax1 is indispensable for zebrafish granulopoiesis. This is the first study demon- strating that hax1 is required for neutrophil development in a vertebrate other than humans. Our data revealed that knockdown of hax1 reduces the expression of cebpa and hcls1 genes, two downstream target genes of the G-csf sig- naling pathway. This result is in agreement with our pre- vious in vitro study, in which knockdown of HAX1 in CD34+ progenitor cells impaired granulocytic differentia- tion by reducing the levels of CEBPA and HCLS1 expres- sion.18 Similarly, CEBPA expression is severely diminished in CN patients with HAX1 deficiency. C/EBPα is a tran- scription factor involved in steady-state granulopoiesis, and regulates G-CSFR expression through a positive feed-
back loop.25 This regulatory relationship between C/EBPα and G-CSFR appears to be evolutionarily conserved between zebrafish and humans because zebrafish cebpa mutants also display reduced g-csfr expression.42 Although we did not provide a direct assessment of G-CSF signaling in zebrafish hax1-deficient neutrophils, the reduced levels of expression of hcls1 and cebpa, two direct target genes of G-CSF signaling, together with decreased g-csfr+ cells in the morphants support the notion that hax1 has a role in G-CSF signaling, which is in agreement with previous in vitro data.18 It is, however, important to stress that our data do not rule out the possibility that hax1 knockdown reduced the number of cebpa-expressing cells rather than decreasing the cebpa expression level in each myeloid cell. Nevertheless, the expression of cebpb was increased in the hax1 morphants. C/EBPb functions as the main transcrip- tional regulator for emergency granulopoiesis,43 and CN patients with HAX1 deficiency also show an elevated level of CEBPB expression.18,44
Previous studies have shown that HAX1 has an anti- apoptotic function and interacts with a variety of intracel-
ABC
DEF
G
H
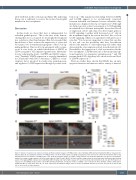
Figure 5. Enhanced apoptosis by hax1 knockdown. (A) Representative images of TUNEL-positive cells in wild-type (WT) and hax1 morphants (MO) at 1 day post-fer- tilization (dpf). (B, C) Quantitative numbers of TUNEL-positive cells in the trunk region at 1 dpf (B) and 2 dpf (C). Note injection of control (CT) morpholino did not sig- nificantly increase the number of TUNEL-positive cells. (D) Representative images of acridine orange-stained cells in WT and hax1 MO at 1 dpf. (E, F) Quantitative numbers of acridine orange-stained cells in the trunk region at 1 dpf (E) and 2 dpf (F). (G) Representative images from the head (top panel) and trunk region (bottom panel) of the tg(lyz:dsRED) embryos injected with hax1 MO showing cells stained with caspase-3/7 reporter (yellow) and neutrophils (red) at 2 dpf. (H) Frequency of caspase-3/7 and dsRED double positive cells in WT and hax1 morphants. n indicates number of dsRED+ cells counted from three wild-type embryos (WT) and 10 morphants (MO) at 2 dpf. Each dot in B, C, E and F represents an individual embryo. Data are means ± standard deviation. Scale bars: 100 mm (A, D) and 50 mm (G). ov: otic vesicle; ye: yolk extension.
haematologica | 2021; 106(5)
1317