Page 89 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 89
Asxl1 lesions collaborate with CEBPA-p30 in AML
AB
C
D
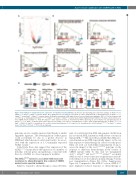
Figure 4. The ASXL1G643W variant affects the expression of leukemia relevant pathways. (A). Volcano plot depicting gene expression changes in Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 vs. Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blasts. (B-C). GSEA plots for selected gene sets which are either upregulated (B) or downregulated (C) in Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 versus Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blasts. (D) Boxplots showing the CHIP-signal levels of selected marks surrounding the TSS (+/- 500 bp) for genes that are either up- or downregulated in Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 vs. Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blasts (Online Supplementary Table S1). The data is derived from a pre- vious CEBPA mutant (Cebpap30/p30, Asxl1 WT) dataset.22 Gene expression levels as determined by RNA sequencing are also indicated. Up: upregulated genes in
Asxl1G643W/G643W vs. Asxl1+/+ leukemic blasts (false discovery rate [FDR] 0.05, log G643W/G643W
Asxl1+/+; (FDR 0.05, log G643W/G643W
+/+
vs. Asxl1 . P-values
FC <0, baseMean >10, n=201), neutral: neutral genes (-0.01 < log levels *P<0.05s, **P=0.01, ***P=0.001 are indicated
2
genotype are also weakly expressed and display a similar epigenetic signature. The downregulation of these genes could potentially be due to a global decrease in H3K4me3 which has previously been found to be associ- ated with the expression of a C-terminally truncated ASXL1 variant.17
Collectively, these data suggest that expression of the ASXL1G643W variant affects the expression of a number of leukemic relevant genes and pathways, consistent with the role of ASXL1 as a broad epigenetic modifier.
The ASXL1G643W variant is associated with increased resistance to chemotherapy in the context of CEBPA mutant acute myeloid leukemia
Failure to respond to chemotherapy is a major determi-
2
2
FC>0, baseMean>10, n=105), down: downregulated genes in Asxl1 vs.
FC<0.01, baseMean>10, n=165) in Asxl1
nant of overall survival in AML and genomic stratification has associated ASXL1 mutations with adverse outcome in human AML.33-35 This raises the possibility that AML-asso- ciated mutations in ASXL1 specifically impact on the cel- lular response to chemotherapy. In order to test this possi- bility, we used our well-defined experimental set-up to assess the impact of the Asxl1G643W/G643W genotype on the response to induction chemotherapy in the context of CEBPA mutant AML. To this end, we transplanted Asxl1+/+; CebpaD/p30 and Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaD/p30 secondary AML (a total of seven clones) into recipient mice and sub- jected them to low-dose induction chemotherapy 3 weeks post transplantation (Figure 5A, Online Supplementary Figure S4). Compared to the ASXL1WT cohort, ASXL1G643W mice displayed reduced response to chemotherapy as
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)
1005