Page 88 - 2021_04-Haematologica-web
P. 88
T. D’Altri et al.
AB
CE
D
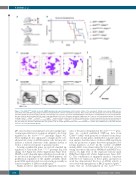
Figure 3. The ASXL1G643W variant accelerate CEBPA mutant acute myeloid leukemia. (A) Schematic outline of the experiment. Briefly, bone marrow (BM) was har- vested from mice with different genotypes and then transplanted into cohorts of irradiated recipients. Three weeks after the transplant, mice were injected with pIpC and subsequently observed for signs of disease development over a period of 60 weeks. (B) Kaplan-Meyer survival curve of transplanted mice. The arrow indicates the time point for injection with pIpC. We used a Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test to determine statistical significance (n>7 mice in each experimental group). (C) Giemsa staining of Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 or Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blasts isolated from the BM of moribund mice. A normal aged-matched mouse was included as a control. (D) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of Asxl1+/+; CebpaΔ/p30 or Asxl1G643W/G643W; CebpaΔ/p30 leukemic blast isolated from transplanted mice. The plot shows the amount of donor-derived c-Kit positive cells. A normal aged-matched mouse was included as a control. (E) Quantification of the data from (D) (n=3 mice in each experimental group).
p53 class mediator) and immune activation (antigen pro- cessing a presentation of exogenous antigen) to be down- regulated in the Asxl1G643W/G643W genotype (Figure 4C). These findings do not only point to changes in the over- all metabolic status of ASXL1 mutant cells, but may also indicate a reduced activation of the immune system as well as a decreased response to genomic insults.
Focusing on individual genes, we noticed a marked up- regulation of Traip in the Asxl1G643W/G643W genotype (log2 fold change =6.7; Figure 4A, Online Supplementary Figure S3A). TRAIP is an E3 ubiquitin ligase which has been shown to be involved in the regulation of the NF-κB pathway, cell proliferation, regulation of the spindle assembly check- point, DNA replication fork recovery and more recently as a master regulator of DNA crosslink repair.28-32
Finally, in order to understand the epigenetic character-
istics of the genes deregulated in the Asxl1G643W/G643W geno- type, we overlaid published ChIP-seq data from CebpaD/p30 AML22 with promoter coordinates from dereg- ulated and constant genes, identified in our gene expres- sion analysis described above. In these ASXL1 proficient cells, the promoters of genes that were upregulated fol- lowing mutation of Asxl1 (in the context of CEBPA mutant AML), were characterized by low levels of “acti- vating” histone modifications H3K4me3 and H3K27ac as well as by high level of the repressive histone mark H3K27me3 (Figure 4D, Online Supplementary Figure S3B- C). This combination of epigenetic marks is consistent with the low expression of these genes and previous work has demonstrated that loss of ASXL1 activity is associated with upregulation of PRC2-repressed genes.5,9 Genes that are down-regulated in the Asxl1G643W/G643W
1004
haematologica | 2021; 106(4)