Page 121 - 2021_03-Haematologica-web
P. 121
Slc35a1 deficiency and thrombocytopenia
ABC
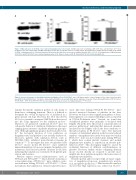
Figure 7. Mpl expression in Slc35a1-/- bone marrow megakaryocytes is decreased. (A) Mpl expression on wild-type (WT) (n=8 mice) and Slc35a1-/- (n=7 mice) megakaryocytes was analyzed with anti-Mpl antibody by western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Quantification of Mpl expression in WT (n=8) and Plt Slc35a1-/- megakaryocytes (n=7) by densitometry of the western blot data. Data are means ± standard deviation (SD). *P<0.05. (C) Quantification of Mpl transcripts in WT (n=6) and Plt Slc35a1-/- bone marrow megakaryocytes (n=6). Data are means ± SD. IB: immunoblot; NS not statistically significant.
AB
Figure 8. Increased clearance of desialylated platelets by Küpffer cells in Plt Slc35a1–/– mice. (A) Representative confocal images of liver cryosections from wild- type (WT) (n=4) and Plt Slc35a1–/– (n=3) mice stained with anti-F4/80 (red) and anti-CD41 (green) antibodies. Scale bar, 25 mm. (B) Quantification of WT (n=3 mice) and Slc35a1–/– (n=3 mice) platelets in the liver per image (40X). Data are means ± standard deviation. ***P<0.001.
regulate the specific sialylation pattern of cells, many of them have overlapping functions. Thus, it is difficult to determine the overall biological role of sialylation in a given specific cell type. However, the CST, encoded by Slc35a1, is essential to transport CMP-SA from the cytosol into the Golgi apparatus for the sialylation process.39 Therefore, we generated conditional Slc35a1f/f mice for cell-specific deletion of sialylation. Sialylation is the major capping glycan structure on platelet membrane glycopro- teins. Although significant progress has been made recent- ly,11 the biological function of total sialylation on megakaryocytes and platelets is not yet fully understood. Moreover, patients with sialylation defects, such as SLC35A1-CDG, exhibited macrothrombocytopenia in common.20-23,40 To investigate this issue, we generated a Plt Slc35a1–/– mouse model. Plt Slc35a1–/– mice exhibited impaired megakaryocytopoiesis, impaired megakaryocyte maturation, and excessive platelet clearance in the liver, indicating that sialylation is essential for both platelet gen- eration and clearance.
Platelets express several sialyltransferases, such as ST3Gal-I and ST3Gal-IV.18,19,41 Macrothrombocytopenia is a major phenotype of Plt Slc35a1–/– mice, which is consis- tent with mice lacking ST3Gal-I or ST3Gal-IV.17,41,42 These data indicate that sialylation is critical for platelet homeo-
stasis. Like mice lacking ST3Gal-IV, Plt Slc35a1–/– mice showed increased clearance of platelets in the liver. However, we did not detect significant numbers of desia- lylated platelets co-localized with hepatocytes as reported in ST3Gal-IV-deficient mice.17 Instead, we found that desialylated platelets were primarily co-localized with Küpffer cells in the liver. This result is consistent with our previous publication,7 indicating that increased clearance mediated by the Küpffer cells in the liver contributes to thrombocytopenia in Plt Slc35a1–/– mice. The increased clearance of desialylated platelets in the liver and reduced numbers of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow found in Plt Slc35a1–/– mice was not found in mice lacking ST3Gal- I, which have normal platelet clearance and normal megakaryocyte number, as reported in an abstract pub- lished in 2014.42 This discrepancy might be caused by redundant functions of different sialyltransferases in platelets. However, further studies comparing different mouse models directly are required to provide more insights into how sialylation regulates the homeostasis of megakaryocytes/platelets.
Thrombopoietin and its receptor Mpl are major regula- tors of megakaryocytopoiesis, megakaryocyte matura- tion, and platelet production.14,43 Our western blot analysis showed that Mpl expression was reduced in Slc35a1–/–
haematologica | 2021; 106(3)
767