Page 65 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 65
CHAPTER 8 - Myeloproliferative neoplasms
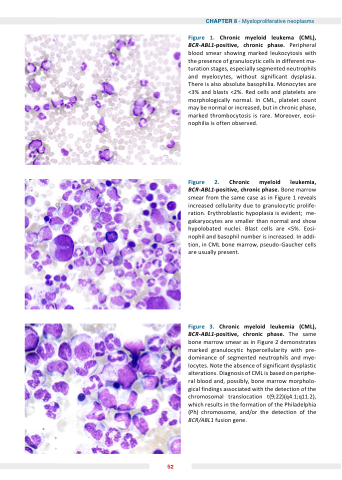
Figure 1 hronic myeloid leu ema ( ML) BCR-ABL1 positive chronic phase Peripheral blood smear showing marked leukocytosis with the presence of granulocytic cells in different ma- turation stages especially segmented neutrophils and myelocytes without significant dysplasia There is also absolute basophilia Monocytes are <3% and and blasts <2% Red cells and and platelets are morphologically normal In CML platelet count may be normal or or increased but in in chronic phase marked thrombocytosis is is rare Moreover eosi- nophilia is often observed Figure hronic BCR-ABL1 positive chronic phase Bone marrow smear from the same case as as in Figure 1 reveals increased cellularity due to granulocytic prolife- ration Erythroblastic hypoplasia is evident me- gakaryocytes are smaller than normal and show hypolobated nuclei Blast cells are <5% Eosi- nophil and basophil number is increased In addi- tion in CML bone marrow pseudo-Gaucher cells are usually present Figure hronic myeloid leu emia ( ML) BCR-ABL1 positive chronic phase The same bone marrow smear as in Figure 2 demonstrates marked granulocytic hypercellularity with pre- dominance of segmented neutrophils and mye- locytes Note the absence of significant dysplastic alterations Diagnosis of CML is is based on on periphe- ral blood and possibly bone marrow morpholo- gical findings associated with the the detection of the the chromosomal translocation t(9 22)(q4 1 1 1 q11 2) 2) which results in the the formation of the the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome and/or the the detection of the the BCR/ABL1 fusion gene myeloid leu emia 52