Page 66 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 66
AB
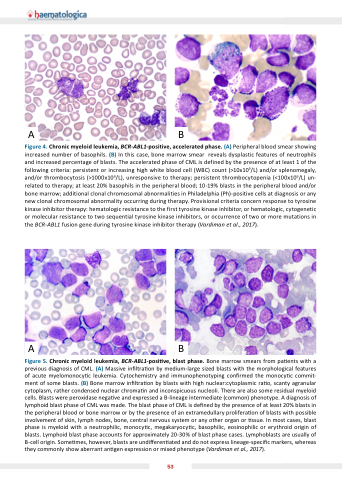
Figure 4 hronic myeloid leu emia BCR-ABL1 positive accelerated phase (A) Peripheral blood smear showing increased number of of basophils (B) In this case bone marrow smear reveals dysplastic features of of neutrophils and increased percentage of of of of blasts The accelerated phase of of of of CML is defined by the the presence of of of of at at least 1 of of of of the the following criteria: persistent or or increasing high white blood cell (WBC) count (>10x109/L) and/or splenomegaly and/or thrombocytosis (>1000x109/L) unresponsive to to to therapy persistent thrombocytopenia (<100x109/L) un- related to therapy at at least 20% basophils in in the the the peripheral peripheral blood blood 10-19% blasts in in the the the peripheral peripheral blood blood and/or bone marrow additional clonal chromosomal abnormalities in Philadelphia (Ph)-positive cells at diagnosis or or any new clonal chromosomal abnormality occurring during therapy Provisional criteria concern response to tyrosine kinase kinase inhibitor inhibitor therapy: hematologic hematologic resistance to to to to to to the the first tyrosine kinase kinase inhibitor inhibitor or or or hematologic hematologic cytogenetic or or or or or molecular resistance to to two two sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitors or or or or or occurrence of two two or or or or or more mutations in in in in the the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene during tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy (Vardiman et al 2017) AB
Figure hronic myeloid leu emia BCR-ABL1 posi ve ve blast blast phase Bone marrow smears from pa ents with with a a a a a a a a a a a a a a previous diagnosis of of CML (A) Massive in in ltra on on on on on on by medium-large sized blasts with with the the morphological features of of of acute myelomonocy c c c c c c c c c c c c c leukemia Cytochemistry and immunophenotyping con rmed the the monocy monocy c c c c c c c c c c c c c commit- ment of of some some blasts blasts (B) Bone marrow in in in ltra on on on on on on on by blasts blasts with high nuclear:cytoplasmic ra ra ra ra o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o o scanty agranular cytoplasm cytoplasm rather condensed nuclear nuclear chroma n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n n and and inconspicuous nucleoli There are also some some residual myeloid cells Blasts were peroxidase nega ve and and expressed a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a B-lineage intermediate (common) phenotype A diagnosis of of of of lymphoid blast blast blast blast phase phase of of of of of of CML CML was made The blast blast blast blast phase phase of of of of of of CML CML is is de de ned by by the the the presence presence of of of of of of at at least 20% blasts blasts in in in the the the the peripheral blood or or or or or bone bone marrow or or or or or by by the the the the presence presence of of of of of of an an an extramedullary prolifera on on on of of of of of of blasts blasts with possible involvement of of of of skin lymph nodes bone bone central nervous system or or or or or or or any other organ or or or or or or or ssue In most cases blast blast phase phase phase is myeloid with a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a neutrophilic monocy c c c c c c c c c c c c megakaryocy c c c c c c c c c c c c basophilic eosinophilic or or or or or or erythroid origin of of of of blasts blasts blasts Lymphoid blast blast blast blast blast phase phase phase accounts for approximately 20-30% of of of blast blast blast blast blast phase phase phase cases Lymphoblasts are are usually of of of B-cell origin Some mes however blasts blasts blasts are are undi eren ated and do not not express express lineage-speci c c c c c c c markers whereas they commonly show aberrant an an an an gen expression or or mixed phenotype (Vardiman et al 2017) 53