Page 63 - Haematologica Atlas of Hematologic Cytology
P. 63
CHAPTER 8 - Myeloproliferative neoplasms
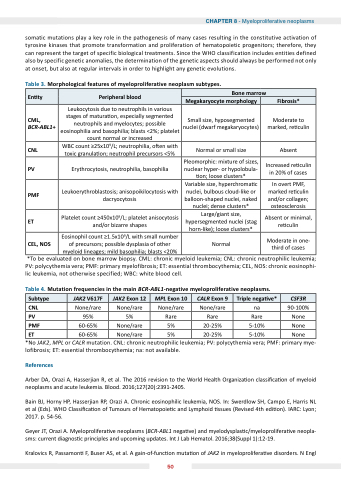
somatic mutations play a a a a a a a a a key role in in in the the pathogenesis of of many cases resulting in in in the the constitutive activation of of tyrosine kinases that promote transformation and proliferation of hematopoietic progenitors therefore they can represent the the target of specific biological treatments Since the the WHO classification includes entities defined also by specific genetic genetic anomalies the the determination of the the genetic genetic aspects should always be performed not only at at onset but also at at regular intervals in in order to highlight any genetic evolutions Table 3 Morphological features of myeloproliferative neoplasm subtypes n ty Peripheral blood one marrow Mega aryocyte morphology
Fibrosis ML BCR-ABL1+
Leukocytosis due to to neutrophils in various stages of matura on especially segmented neutrophils and and myelocytes possible eosinophilia and and basophilia blasts <2% platelet count normal or or increased Small size hyposegmented nuclei (dwarf megakaryocytes)
Moderate to marked re culin
CNL
WBC count ≥25x109/L neutrophilia o o o o o o o en with toxic granula on neutrophil neutrophil precursors <5%
Normal or or small size Absent
PV
Erythrocytosis neutrophilia basophilia Pleomorphic: mixture of sizes nuclear hyper- or or hypolobula- on loose clusters*
Increased re re culin
in in 20% of cases PMF
Leukoerythroblastosis anisopoikilocytosis with dacryocytosis
ariable size hyperchroma c c c c nuclei nuclei bulbous cloud-like or balloon-shaped nuclei nuclei nuclei naked nuclei nuclei dense clusters*
In overt PMF
marked re culin
and/or collagen osteosclerosis
ET
Platelet count ≥450x109/L platelet anisocytosis and/or bizarre shapes
Large/giant size hypersegmented nuclei (stag horn-like) loose clusters*
Absent
or minimal re culin
L S Eosinophil count ≥1 5x109/L with small number of of precursors possible dysplasia of of other myeloid myeloid lineages mild basophilia blasts <20%
Normal Moderate in one- third of cases *To be evaluated on on on on on bone marrow biopsy CML: chronic chronic chronic myeloid myeloid leukemia leukemia CNL: chronic chronic chronic neutrophilic leukemia leukemia PV: polycythemia vera PMF: primary myelofibrosis ET: essential thrombocythemia
CEL NOS: chronic chronic chronic eosinophi- lic leukemia not otherwise specified WBC: white blood cell Table 4 Mutation fre uencies in in the main BCR-ABL1 negative myeloproliferative neoplasms
*No JAK2 MPL or CALR mutation CNL: chronic neutrophilic leukemia P P P : : : polycythemia vera PMF: primary mye- lofibrosis ET: essential thrombocythemia
na: not available References
Arber DA Orazi A A A Hasser ian R et al al The 2016 2016 revision to the World Health Organiza on on on classi ca on on on of myeloid neoplasms
and acute leukemia Blood 2016 2016 127(20):2391-2405 Bain BJ Horny HP Hasser ian RP Orazi A A Chronic eosinophilic leukemia NOS In: Swerdlow SH Campo E E Harris NL
et al (Eds) WHO Classi ca on on on on of of Tumours of of Hematopoie c c c c and Lymphoid ssues (Revised 4th edi on) IARC: Lyon 2017 p 54-56 Geyer JT Orazi A A Myeloprolifera ve ve ve neoplasms
(BCR-ABL1 nega ve) and and myelodysplas c/myeloprolifera ve ve ve neopla- sms: current diagnos c c c c c principles and and upcoming updates Int J J Lab Hematol 2016 38(Suppl 1):12-19 Kralovics R Passamon F Buser AS et al al A A A gain-of-func on on on muta on on on of of JAK2 in in myeloprolifera ve disorders N Engl
Subtype
JAK2 V617F
JAK2 xon 1 MPL xon 10 CALR xon Triple nega ve CSF3R
CNL
None/rare
None/rare
None/rare
None/rare
na 90-100%
PV
95%
5%
Rare
Rare
Rare
None PMF
60-65%
None/rare
5%
20-25%
5-10%
None ET
60-65%
None/rare
5%
20-25%
5-10%
None 50