Page 165 - 2019_03-Haematologica-web
P. 165
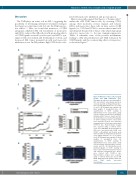
Maraviroc inhibits cHL crosstalk and xenograft growth
Discussion
The TME plays an active role in cHL,11 suggesting the possibility of developing alternative treatment strategies that target not only tumor cells, but also the TME’s protec- tive effects.11,22 Here, we found that maraviroc, a CCR5 antagonist, inhibited cHL cell recruitment of monocytes and MSCs, reduced the cHL cell growth-promoting effects of CCR5 ligands secreted by monocytes and MSCs, syn- ergized with doxorubicin and brentuximab vedotin, and decreased cHL tumor xenograft growth and monocyte infiltration in vivo. In cHL patients, high CCL5 levels corre-
lated with monocyte infiltration and poor prognosis.
Our in vitro results suggest that there is a “domino effect” within the cHL TME: tumor cells, by secreting CCL5, among other molecules, recruit, expand, and educate MSCs and monocytes; these cells, in turn, secrete CCR5 ligands (i.e., CCL3 and CCL4) to recruit other normal cells and stimulate the growth of tumor cells, which reprogram (educate) monocytes to become immunosuppressive TAMs. A schematic view of the possible mechanisms leading to cHL cell proliferation and TME formation by CCR5 ligands, and the counteracting effects of maraviroc,
is shown in Figure 7.
A
B
C
D
EF
Figure 5. Maraviroc reduces cHL xenograft growth and TAM infiltration. (A-D) Xenografts in nude mice inoculated with L- 540 cells (20x106 cells/animal) and treat- ed every day with an intraperitoneal injec- tion of 10 mg/kg maraviroc (n = 5) or vehi- cle (n=5). (A) Xenograft tumor growth. (B) Body weights of xenografted mice. (C) Quantification of CD68+ staining in immunofluorescent cryosections using Volocity software provided by PerkinElmer (arbitrary units). Data are means and SD. (D) Immunofluorescent photomicrographs of CD68+ staining in tumor cryosections from maraviroc-treated and untreated xenografted mice. Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO-3 dye. Representative images were acquired using a confocal micro- scope (Leica DM IRE2). (E-H) Xenografts in NSG mice inoculated with L-428 cells (10x106 cells/animal) and treated every other day with an intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg maraviroc (n = 5) or vehicle (n=5). (E) Xenograft tumor growth. (F) Body weights of xenografted mice. (G) Quantification of CD68+ staining in immunofluorescent cryosections using Volocity software (arbitrary units). Data are means and SD. (H) Immunofluorescent photomicrographs of CD68+ staining in tumor cryosections from maraviroc-treated and untreated xenografted mice. Nuclei were stained with TO-PRO-3 dye. Representative images were acquired using a confocal microscope (Leica DM IRE2). NSG: NOD/SCID gamma chain defi- cient; TAM: tumor associated macrophages.
GH
haematologica | 2019; 104(3)
571