Page 169 - Haematologica-April 2018
P. 169
3D reconstructed myeloma microenvironments
(Figure 4D). Accordingly, the protection conferred by L- VCAM1 was highly significant in both 2D and 3D condi- tions, particularly in the latter (Figure 4C).
Finally, the involvement of soluble factors in promoting drug resistance in our system was investigated using the well-described model of dexamethasone-treated MM1.S cells, where IL-6 is recognized to exert a protective effect.30 As reported,27 the cytokine specifically triggered STAT3 pathway in MM1.S cells, as indicated by western blot analysis and inhibition experiments with the anti-IL-6R monoclonal antibody tocilizumab (TCZ) (Online Supplementary Figure S4A), and also protected MM1.S cells from dexamethasone-induced death (Figure 4E), both in 2D and in 3D conditions. To further support this finding, a viability assay was performed (Online Supplementary Figure S4B), showing that IL-6 significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of dexamethasone.
3D culture supports primary MM cells survival and functions
Isolated primary MM cells outside their native microen- vironment do not survive. We exploited our model using
primary MM cells from patients, with the major aim of promoting their survival. We took advantage of MM BM stroma and HUVEC onto which primary isolated CD138- MM cells were seeded and cultured in bioreactor for up to seven days. In the resulting constructs viable MM cells could be identified which retained the expression of line- age-specific markers as well as light chain production (Figure 5A). To address the role of cell-cell interactions, we compared the expression of β1 integrin in 2D and 3D par- allel experiments. β1 integrin was up-regulated in scaf- folds, and this upregulation was paralleled by down- stream Akt phosphorylation (Figure 5B). STAT3 phospho- rylation was also increased in 3D compared 2D co-cul- tures and could be attributed almost exclusively to MM cells (Figure 5C). Accordingly, when primary MM cells from 7 newly diagnosed patients were co-cultured with a pool of allogeneic BMSC plus HUVEC, the number of cells retrieved from the scaffolds at the end of culture matched the input number (Figure 5D), at variance with parallel 2D co-cultures. Moreover, both MM cells and stroma retained their specialized functions, as indicated by β2-microglob- ulin and soluble factors released in the supernatant from
AB
CD
E
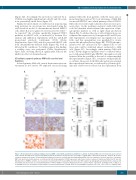
Figure 6. Bortezomib affects primary multiple myeloma (MM) cells viability and functions within the scaffolds. (A) Primary MM cells from 6 patients were retrieved from scaffolds after 48 hours of bortezomib (BTZ) treatment; death was calculated as the percentage of CD38+/AnnV+ cells by flow cytometric analysis. (B) A repre- sentative experiment is shown. (C) Immunohistochemistry performed on scaffolds populated with primary MM cells from 2 patients reveals the presence of apoptotic MM cells upon bortezomib exposure, as indicated by both down-regulated CD138 expression and intense nuclear caspase-3 immunoreactivity. Bar=50 mm. (D) Metalloprotease (MMPs) activities are measured in supernatants from treated (BTZ) and untreated (NT) samples by zymography and densitometric analyses (left and middle panels). Results are mean±Standard Error of Mean (SEM) of 6 patients. Right panel shows a representative experiment. (E) Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), IL- 6 and VEGF levels are determined in supernatants of treated and untreated scaffolds. Data are mean±SEM of 6 patients.*P≤ 0.05; **P≤ 0.01. a.u.: arbitrary units.
haematologica | 2018; 103(4)
713