Page 26 - Haematologica3
P. 26
386
J.T. Butler et al.
that provide dynamic regulation of hematopoiesis to assure the adequate formation and function of mature blood cells from HSCs.1 Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), their osteoprogenitor cell progeny, as well as endothelial cells and adipocytes coordinately maintain hematopoiesis by regulating proliferation, quiescence, differentiation, and apoptosis of HSPCs through juxtacrine and paracrine activity.2 Changes in compartmental oxygen concentra- tion, hemorrhage, chemotherapy and irradiation can all prompt the emergence of HSCs from quiescence,47,48 and
several lines of evidence suggest that EVs are involved in regulating BM function during homeostasis and in response to injury (Table 2A, Figure 2).
Some of the earliest descriptions of EVs revealed their role as platelet-derived anti-hemophilic particles and in transferrin receptor release from sheep reticulocytes.9 Additionally, more recent evidence points to EVs as important physiological mediators of signaling across the immunological synapse.11,49 Yet, much less is known about how vesicles might contribute to steady-state
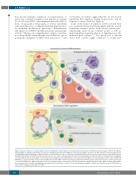
Figure 2. Current evidence for extracellular vesicle crosstalk in the homeostatic bone marrow microenvironment. (A) MSC-derived EVs signal to HSPCs through the TLR-4 pathway, resulting in myeloid biased expansion. (B) Megakaryocyte-derived MVs are internalized by HSPCs and increase differentiation of new megakaryocytes through RNA-mediated signaling. (C) Hypoxia induces erythroleukemia cells to release EVs containing miR-486 which increases erythroblastic differentiation by tar- geting Sirt1 in HSPCs. (D) G-CSF infusion stimulates the release of EVs containing miR-126 that act to down-regulate VCAM-1 in HSPCs, resulting in their mobilization out of the BM. (E) HSPCs autoregulate stem potential by packaging and releasing critical secretory proteins through the exosomal pathway via the action of VPS33B. ANGPTL-2/3; angiopoietin-like protein 2 and 3; BM: bone marrow; CMP: common myeloid progenitor; EB: erythroblast; EVs: extracellular vesicles; G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GMP; granulocyte monocyte progenitor; HSPC: hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell; Mk: megakaryocytes; MkB: megakaryoblast; MSC: mesenchymal stem cell; miR: microRNA; MV: microvesicles; TLR-4: Toll-like receptor 4; TPO: thrombopoietin; VCAM-1: vascular cell adhesion molecule; VPS33B: vac- uolar protein sorting-associated protein 33B.
haematologica | 2018; 103(3)