Page 27 - Haematologica3
P. 27
EVs in the hematopoietic microenvironment
hematopoietic function or during a regenerative BM Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor mobilization is response. EV release is very clearly subject to a range of one such stimulus that appears to increase vesicle release cellular stimuli, including cytokine activation, ionizing from hematopoietic progenitors.52 Following injury, EV radiation, and differences in tissue oxygen tension.50,51 release may promote the selective delivery of miRNAs
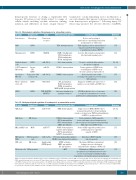
Table 2A. Physiological regulation of hematopoiesis by extracellular vesicles.
EV origin
Reticulocytes
MSCs
Megakaryocytes
Erythroleukemia cells
G-CSF stimulated BM stroma
Recipient cell
Macrophage
HSPCs
HSPCs
HSPCs
Stroma ECs HSPCs
Cargo
Transferrin receptor
Mk-RNA
miR-486-5p miR-126
miR-183-5p
Wnt3, Oct4,
TPO, ANGPTL2, ANGPTL3
Molecular target and effect
TLR4: binding/activation
ICAM-1: binding/entry CD63: binding/entry CD18: binding/entry CD11b: binding/entry
Sirt1: downregulation VCAM-1: downregulation
HMOX1: downregulation
SCL: upregulation, HoxB4: upregulation GATA2: upregulation MAPK p24/44: phosphorylation
Autocrine signaling loop: maintains stemness
Functional event
Release and recycling of transferrin receptor during enucleation and maturation of erythrocytes
TLR4 signaling results in myeloid biased expansion and skewed hematopoietic repopulation potential of HSPCs
Selective differentiation of progenitors into functional megakaryocytes
Promotes erythroid differentiation in response to hypoxia
Down regulation of VCAM1 leads to mobilization of HSPCs out of the niche and into peripheral blood
Reduced proliferative ability
of stromal cells and decreased osteogenic differentiation
Expansion of HSPCs and expression of markers associated with early HSC states
VPS33B mediated release of exosomes
is required for maturation of secretory growth factors and maintaining cell stemness
Functional event
Reference
[9]
[17]
[61]
[63, 64] [52]
[65]
[66]
[45]
Reference
[13, 51]
[14]
[70]
[71] [72]
[73]
Aged mouse BM cells
Young mouse BM stromal cells
Mouse embryonic stem cells
HSPCs
HSPCs
HSPCs
Table 2B. Pathophysiological regulation of hematopoiesis by extracellular vesicles.
EV origin
AML blasts
AML blasts
Recipient cell
HSCPs
BM Stroma
Cargo
miR-150/155
miR-7977
miR-10a/15a
Amphiregulin (EGFR-ligand)
Molecular target and effect
cMYB; downregulation
CXCL12: downregulation SCF: downregulation IGF1: downregulation DKK1: upregulation
PCBP1: downregulation Jagged1: downregulation SCF: downregulation ANGPT1: downregulation
P53: transcriptional dysregulation MDM2: transcriptional dysregulation
EGFR: activation MMP9: upregulation IL8: upregulation
c-MET
AML and MDS cells MSCs
MDS patient CD34+ progenitor MSCs cells
CML cells BM stroma
Melanomacells BMprogenitors
Suppression of cMYB in HSPC reduces clonogenicity and leads to down regulation
of niche retention factor CXCL12 and mobilization of HSPCs to peripheral blood
Down regulation of HSC-supportive factors and suppression of hematopoiesis and osteolineage development by upregulating Dkk1 expression in BM stroma
Reduced HSC-supportive growth factors and hematopoiesis-supportive capacity of MSCs
Alteration of HSCPs viability and clonogenicity
Alteration of BM microenvironment leading to increase attachment
and proliferative advantage of CML cells
MobilizationofBMprogenitorsand upregulation of proinflammatory molecules
at sites of macrophage trafficking leading
to promotion of melanoma invasion and metastasis
AML: acute myeloid leukemia; ANGPT1: angiopoietin 1; ANGPTL2/3: angiopoietin-like protein 2/3; BM: bone marrow; CML: chronic myelogenous leukemia; EC: endothelial cell; EGFR: epithelial growth factor receptor; EV: extracellular vesicle; G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; HMOX: heme-oxygenase molecule 1; HSC: hematopoietic stem cell; HSPCs: hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; IGF1: insulin-like growth factor 1; IL8: interleukin 8; Mk: megakaryocyte; MDS: myelodysplastic syndrome; miR: micro-ribonucleic acid; Mk: megakaryocyte; MSC: mesenchymal stem cell; MMP9: matrix metalloprotease 9; SCF: stem cell factor; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4;TPO: thrombopoietin;VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1;VPS33B: vacuolar protein sorting 33B.
haematologica | 2018; 103(3)
387