Page 162 - 2020_08-Haematologica-web
P. 162
L.M. Jonart et al.
AB
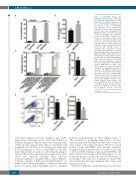
Figure 6. Me6TREN disrupts the meningeal-leukemia niche and attenu- ates leukemia chemoresistance in vitro and in vivo. (A) NALM-6 leukemia cells were co-cultured with meningeal cells in the presence or absence of Me6TREN 100 mM. After 24 h, non-adherent leukemia cells were removed and quanti- fied. (B) Mice were transplanted with NALM-6 leukemia cells (2x106 cells; n=5 per group). After 16 days, mice were treated with Me6TREN 10 mg/kg subcu- taneous or phosphate-buffered saline control for 3 days. After an additional 24 h, 5-10 mL of cerebrospinal fluid were removed from the cisterna magna and leukemia cells were quantified using flow cytometry and counting beads. (C) Leukemia cells in suspension or co-cul- tured with primary meningeal cells were treated with Me6TREN ± cytarabine 500 nM and after 48 h viability was assessed with annexin-V staining and flow cytome- try. (D-G) Mice transplanted with NALM-6 (2x106 cells; n=5 per group; D & E), Jurkat (2x106 cells; n=5 per group; F), or primary B-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (PRoXe Sample CBAB-62871-V1; 1x106 cells; n=5 per group; G) cells were treated with cytarabine (50 mg/kg intraperitoneal) or cytarabine + Me6TREN (10 mg/kg subcu- taneous). Forty-eight hours after complet- ing therapy mice were euthanized, the heart was perfused, the meninges were isolated, dissociated and stained with human CD19 (NALM-6 & PDX) or CD3 (Jurkat) antibody, and leukemia cells were quantified by flow cytometry and counting beads (D, F, G). Representative flow plots for NALM-6 are shown in (E). For all graphs, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 by analysis of variance or a t-test.
C
D
EFG
cell-surface/adhesion proteins VCAM-1 and CD99. Supporting a functional role for CD99 and VCAM-1 in leukemia-meningeal adhesion, antibodies targeting either of these proteins attenuated the adhesion of leukemia and meningeal cells. CD99 has not been previously implicated in the mechanism of action of Me6TREN or the ALL niche. Importantly, in addition to directly participating in cell-cell adhesion through homo/heterotypic interactions, CD99 also regulates multiple other adhesion molecules/pathways including LFA-1, a4b1, ELAM-1, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, MMP, and CXCR4/CXCL12.55 As many of these adhesion pathways contribute to the bone marrow leukemia niche, Me6TREN may also diminish
leukemia chemoresistance in other leukemia niches.53,56 This possibility is potentially supported by our data demonstrating that Me6TREN extended the overall sur- vival of mice treated with cytarabine. However, if upon further testing Me6TREN only disrupts leukemia- meningeal adhesion and the effect on survival is due only to decreased CNS leukemia progression, Me6TREN could still be effective in treating isolated CNS relapses, for use in upfront therapy to reduce the risk of CNS relapse, or potentially to reduce the dose or intensity of current CNS- directed therapies that carry significant risks of short- and long-term toxicity.
Given the complexity of cell-cell interactions, this mul-
2138
haematologica | 2020; 105(8)