Page 156 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 156
C.R. Soderquist et al.
nine (66%) patients are alive with persistent disease and three (33%) have died; one (case 5) due to septicemia and multiorgan failure following chemotherapy-induced intes- tinal perforation 1 year after diagnosis and two (cases 4 and 9) due to disease transformation 11 and 27 years after diagnosis.
Morphological features
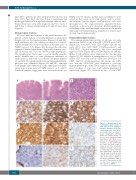
All cases with involvement of the small intestines dis- played a dense diffuse or nodular infiltrate of small-sized lymphocytes in the lamina propria (Figures 1A and 2A), with extension into the submucosa noted in a subset. Villous atrophy was observed in three of the nine cases of ITLPD (cases 2, 4, 9) (Figure 1B), however the villi were expanded (blunted appearance) (Figure 2B) in many cases, and all except one (case 10) showed crypt hyperplasia. The lymphocytes had round, ovoid or mildly irregular nuclei, variable fine or coarse chromatin, indistinct or small nucleoli, and scant or moderate cytoplasm (Figures 1C and 2C). No significant increase in intraepithelial lym- phocytes was identified (Figures 1B and 2B), although focal lymphocytic infiltration of the epithelium was pres- ent in four of nine cases of ITLPD (cases 1, 2, 4, and 7). Scattered lymphoid aggregates were seen in all except one
ITLPD (case 5). Sparse, patchy mucosal infiltrates were noted in the seven cases with gastric and/or colonic involvement. Mitotic figures and apoptotic cells were inconspicuous. No angiocentricity, angiodestruction, ulceration, or necrosis was observed. The histopathologi- cal findings of the small intestinal biopsy from one patient with large cell transformation, available for review (case 4), were reported previously.11
Immunophenotypic features
The immunophenotypic profiles of all cases are sum- marized in Table 2. Four of ten (40%) ITLPD were CD4+ (Figure 1D), four (40%) were CD8+ (Figure 2D) and one each (10%) was CD4+/CD8+ (“double-positive”) and CD4-/CD8- (“double-negative”). All cases analyzed expressed CD2 (Figure 1E) and CD3 (Figures 1F and 2E). Other T-cell antigens were expressed by the majority (Figure 1G, H); variable downregulation or loss of CD5 and/or CD7 was seen in four of ten cases (2/4 CD4+, 1/4 CD8+, and 1/1 double-negative). All except one CD8+ case and the CD4-/CD8- case displayed a cytotoxic immunophenotype, with TIA-1 expression (Figure 2F) noted in three of four cases and variable granzyme B expression (Figure 2G) observed in two of four CD8+
ABC
DEF
GHI
Figure 1. Morphological and immunophenotypic features of CD4+ indolent T-cell lymphopro- liferative disorders of the gas- trointestinal tract. (A) A duode- nal biopsy (case 2) shows a dense lymphocytic infiltrate within the lamina propria, as well as villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia. (B) There is no increase in intraepithelial lym- phocytes. (C) The lymphocytes are small and have round to ovoid nuclei, fine chromatin,
JKL indistinct or small nucleoli, and moderate pale pink cytoplasm. The lymphocytes express (D) CD4, (E) CD2, (F) CD3, (G) CD5, and (H) CD7. (I) The neoplastic cells do not express CD103. (J) The Ki-67 proliferation index is low (<5%). The majority of cells are (K) T-bet+, however, 50%
also express (L) GATA3.
1898
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)