Page 155 - 2020_07-Haematologica-web
P. 155
Genetic alterations in indolent GI T-cell LPD
nal lymphadenopathy (55%), bowel wall thickening (33%), and dilated bowel loops (33%). Biopsy-proven sites of disease included the small intestine (90%), colon (60%), stomach (40%), bone marrow (30%, one case only
had cytogenetic evidence of disease), and inguinal lymph nodes (20%). Seven of nine (77%) patients received ther- apeutic interventions consisting of steroids and/or chemotherapy; two were monitored expectantly. Six of
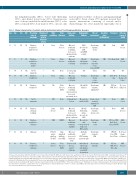
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of patients with gastrointestinal indolent T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.
Case Age Sex Eth Presenting signs &
Duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis (years)
Other conditions
Prior diagnosis
Endoscopic findings
Radiographic findings
Sites of involvement†
Ann Arbor stage
(at diagnosis)
Treatment
Outcome (cause of death)
symptoms
1* 53
2* 50
3 64
4*† 37
5 62
6 41
7 38
8 38
9† 41
10 49
M W Diarrhea, 16 None Celiac Mucosal Mild Duodenum, IEB Bud AWD,
F W
weight loss, night sweats
Diarrhea, weight loss, abd pain, fatigue
3
None
disease
Celiac disease
nodularity, scalloping, decreased duodenal folds, erythema
Mucosal nodularity, scalloping
mesenteric jejunum, LAD, ileum
mild FDG activity
SB wall Duodenum, thickening ileum,
and dilation appendix, colon,
stomach, BM‡
IEB
Pral, Romi, Bud
9 years
AWD, 7 years
F NA NoGI symptoms
0 NA None Sessilepolyp NA Colon NA NA NA in colon
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
W
H
Diarrhea, weight loss
Diarrhea, weight loss
2 None Celiac Mucosal Normal Duodenum, IEB
Bud, Pred, Aza
CP, Dox, VCR, Pred
None
None
CP, Dox, VCR, Bud, Pred, Etop, AGS67E
IFN, CP, Dox, VCR, Pred, Gem
CP, Dox, VCR, Pred, Mes, Aza
D, 11 years (Large cell trans)
D, 1 year (SB perf)
AWD, 1 year
AWD, 21 years
AWD, 7 years
D, 27 years (Large cell trans)
AWD, 19 years
NA NoGI symptoms
W Diarrhea, abd pain, vomiting
NA
0
5
5
3
5
NA
MG
Lyme disease
disease
Celiac disease, EATL
None
EATL
nodularity, scalloping
Mucosal nodularity, scalloping, mosaic pattern, increased vascularity, ulcer
Polypoid ileal lesions
Mucosal nodularity, decreased duodenal folds, gastric erythema
SB and LB dilation
Mesenteric and iliac LAD
SB wall thickening, intuss, mesenteric LAD
ileum,
colon,
stomach
Duodenum, IEB jejunum,
inguinal LN
Ileum, colon, IVE stomach,
inguinal LN,
BM
Duodenum, IE jejunum,
ileum, colon
Duodenum, IEB ileum,
colon
Duodenum, IE stomach,
BM
Duodenum, IEB jejunum
H
A
Diarrhea, weight loss, abd pain
Abd pain
CHD MEITL Mucosal Mesenteric
W Diarrhea, weight loss,
abd pain
PUD, H. pylori, viral hep (B & C)
Crohn disease§
Atyp lymphoid infiltrate, favor MZL
Celiac disease, EATL
nodularity, erythema, friability
Mucosal nodularity, decreased duodenal folds
Flattened SB mucosa, gastric erythema
and retroperitoneal LAD, incr FDG activity
Abd LAD, mild FDG activity, splenomegaly
Mild SB wall thickening and dilation, partial SB obstruction
A: Asian; abd: abdominal; AGS67E: anti-CD37 monoclonal antibody AGS67E; AWD: alive with disease; Aza: azathioprine; BM: bone marrow; Bud: budesonide; CHD: congenital heart disease; CP: cyclophosphamide; D: dead; Dox: doxorubicin; EATL: enteropathy associated T-cell lymphoma; Eth: ethnicity; Etop: etoposide; F: female; FDG: fluorodeoxyglucose; Gem: gemcitabine; GI: gastroin- testinal; H: Hispanic; hep: hepatitis; IFN: interferon; incr: increased; intuss: intussusception; LAD: lymphadenopathy; LB: large bowel; LN: lymph node; M: male; MEITL: monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma; Mes: mesalamine; MG: monoclonal gammopathy; MZL: marginal zone lymphoma; NA: not available; perf: perforation; PUD: peptic ulcer disease; Pral: pralatrexate; Pred: prednisone;Romi:romidepsin;SB:small bowel;trans:transformation;VCR;vincristine;W:White.*Previously published cases.†Findings prior to large cell transformation.‡Bone marrow involvement was detected by cytogenetic analysis; there was no morphological or immunophenotypic evidence of disease and TCRβ polyclonal chain reaction showed polyclonal products. §Biopsies diag- nosed as Crohn disease were not reviewed by authors.
haematologica | 2020; 105(7)
1897