Page 257 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 257
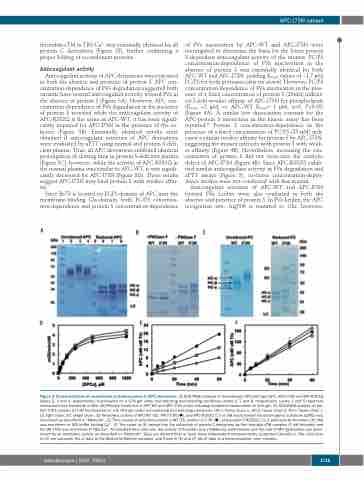
APC-I73N variant
thrombin-sTM in TBS/Ca2+ was essentially identical for all protein C derivatives (Figure 2F), further confirming a proper folding of recombinant proteins.
Anticoagulant activity
Anticoagulant activity of APC derivatives was evaluated in both the absence and presence of protein S. APC con- centration-dependence of FVa degradation suggested both variants have normal anticoagulant activity toward FVa in the absence of protein S (Figure 3A). However, APC con- centration-dependence of FVa degradation in the presence of protein S revealed while the anticoagulant activity of APC-R352Q is the same as APC-WT, it has been signifi- cantly impaired for APC-I73N in the presence of the co- factor (Figure 3B). Essentially identical results were obtained if anticoagulant activities of APC derivatives were evaluated by aPTT using normal and protein S-defi- cient plasma. Thus, all APC derivatives exhibited identical prolongation of clotting time in protein S-deficient plasma (Figure 3C); however, while the activity of APC-R352Q in the normal plasma was similar to APC-WT, it was signifi- cantly decreased for APC-I73N (Figure 3D). These results suggest APC-I73N may bind protein S with weaker affin- ity.
Since Ile73 is located on EGF1-domain of APC near the membrane-binding Gla-domain, both PC/PS concentra- tion-dependence and protein S concentration-dependence
of FVa inactivation by APC-WT and APC-I73N were investigated to determine the basis for the lower protein S-dependent anticoagulant activity of the mutant. PC/PS concentration-dependence of FVa inactivation in the absence of protein S was essentially identical for both APC-WT and APC-I73N, yielding Kd(app) values of ~1.7 μM PC/PS for both proteases (data not shown). However, PC/PS concentration-dependence of FVa inactivation in the pres- ence of a fixed concentration of protein S (20nM) indicat- ed 2-fold weaker affinity of APC-I73N for phospholipids (Kd(app) =2 μM; vs. APC-WT Kd(app)= 1 μM, n=3, P<0.05) (Figure 4A). A similar low dissociation constant for the APC-protein S interaction in the kinetic assay has been reported.28 Protein S concentration-dependence in the presence of a fixed concentration of PC/PS (25 μM) indi- cated a similar weaker affinity for protein S by APC-I73N, suggesting the mutant interacts with protein S with weak- er affinity (Figure 4B). Nevertheless, increasing the con- centration of protein S did not overcome the catalytic defect of APC-I73N (Figure 4B). Since APC-R352Q exhib- ited similar anticoagulant activity in FVa degradation and aPTT assays (Figure 3), co-factor concentration-depen- dence studies were not conducted with this mutant.
Anticoagulant activities of APC-WT and APC-I73N toward FVa Leiden were also evaluated in both the absence and presence of protein S. In FVa Leiden, the APC recognition site, Arg506 is mutated to Gln; however,
A
BC
DEF
Figure 2. Characterization of recombinant activated protein C (APC) derivatives. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant APC-wild type (WT), APC-I73N and APC-R352Q (lanes 2, 3 and 4, respectively), fractionated on a 10% gel under non-reducing and reducing conditions (lanes 6, 7 and 8, respectively). Lanes 1 and 5 represent molecular mass standards in kDa. (B) PNGase treatment of APC-WT and APC-I73N under reducing conditions fractionated on 10% gel. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of pro- tein C-WT, protein C-I73N fractionated on a 8.75% gel under non-reducing and reducing conditions. HC-α: heavy chain α; HC-β: heavy chain β; HC-γ: heavy chain γ; LC: light chain; SC: single chain. (D) Amidolytic activity of APC-WT (), APC-I73N (), and APC-R352Q () (5 nM each) toward the chromogenic substrate SpPCa was monitored as described in “Methods”. (E) Time course of activation protein C-WT (), protein C-I73N (), and protein C-R352Q () (1 μM each) by thrombin (10 nM) was monitored in TBS buffer lacking Ca2+. (F) The same as (E) except that the activation of protein C derivatives by the thrombin-sTM complex (1 nM thrombin and 50 nM sTM) was monitored in TBS/Ca2+. At indicated time intervals, the activity of thrombin was inhibited by antithrombin and the rate of APC generation was deter- mined by an amidolytic activity as described in “Methods”. Data are derived from at least three independent measurements (±standard deviation). The solid lines in (D) are computer fits of data to the Michaelis-Menten equation, and those in (E) and (F) fits of data to a linear equation. min: minutes.
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)
1715