Page 141 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 141
Follicular helper T cells in FL
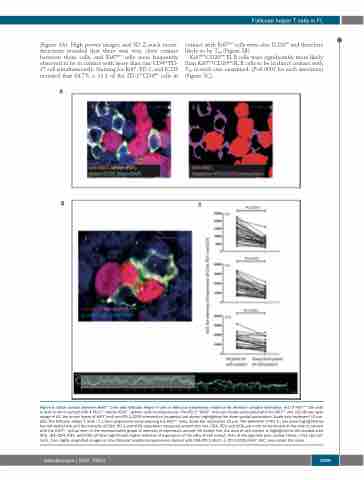
(Figure 3A). High power images and 3D Z-stack recon- structions revealed that there was very close contact between these cells, and Ki67pos cells were frequently observed to be in contact with more than one CD4posPD- 1Hi cell simultaneously. Staining for Ki67, PD-1, and ICOS revealed that 84.7% ± 11.1 of the PD-1HiCD4pos cells in
contact with Ki67pos cells were also ICOSpos and therefore likely to be TFH (Figure 3B).
Ki67posCD20pos FL B cells were significantly more likely than Ki67negCD20pos FL B cells to be in direct contact with TFH in each case examined, (P<0.0001 for each specimen) (Figure 3C).
A
B
P<0.0001
P<0.0001
P<0.0001
Figure 5. Close contact between Ki67pos cells and follicular helper T cells in follicular lymphoma: evidence for immune synapse formation. (A1) A Ki67pos cell (red) is seen to be in contact with 4 PD-1pos (white) ICOSpos (green) cells simultaneously. The PD-1posICOSpos cells are closely associated with the Ki67pos cell. (A2) Binary layer image of A1, the binary layers of Ki67 (red) and PD-1/ICOS intersection (magenta) are shown highlighting the close spatial association. Scale bars represent 10 μm. (B1) The follicular helper T cells ( TFH) form projections encompassing the Ki67pos cells. Scale bar represents 10 μm. The perimeter of the TFH has been highlighted by the red dotted line and the intensity of CD4, PD-1 and ICOS have been measured around this line. CD4, PD1 and ICOS are more concentrated at the pole in contact with the Ki67pos cell as seen in the representative graph of intensity of expression around the dotted line, the area of cell contact is highlighted in the shaded area (B2). (B3) CD4, PD1, and ICOS all have significantly higher intensity of expression at the sites of cell contact than at the opposite pole, paired t-tests, n=61 cell con- tacts, from highly magnified images in nine follicular lymphoma specimens stained with CD4/PD-1/Ki67, or PD-1/ICOS/Ki67. AUC: area under the curve.
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)
1599