Page 121 - Haematologica - Vol. 105 n. 6 - June 2020
P. 121
DNA methylation in T-ALL
patients with low methylation levels had higher CIR (sub- distribution hazard ratio [SHR] 1.87, 95% CI: 1.03-3.38, P=0.04; Table 2 and Figure 4A) and a shorter overall sur- vival (OS) (hazard ratio [HR] 1.78, 95% CI: 1.06-2.98, P=0.03; Table 2 and Figure 4B). In multivariate analysis for CIR, the only prognostic factor to be significantly associ- ated with a reduced CIR was the NOTCH1/FBXW7/RAS/PTEN molecular classifier. However, in multivariate analysis for OS, including age, WBC at diagnosis, central nervous system (CNS) involve- ment, prednisone response, the molecular classifier, and the methylation level as covariates, a low methylation was still independently associated with a higher risk of death (HR 1.79, 95% CI: 1.00-3.19, P=0.05; Table 2).
Discussion
Despite recent insights into the molecular and cellular mechanisms responsible for T-ALL onset and progression, survival rates remain around 50% in adults, justifying the search for novel therapeutic options or more adapted/per- sonalized regimens. The present study focused on pro- moter DNA methylation in a large series of adult T-ALL. As previously reported in pediatric T-ALL,9-11 we showed that DNA methylation status is also a prognostic factor in adult T-ALL. Similarly, patients with a hypoM profile dis-
play an unfavorable outcome compared to hyperM patients. Importantly, even if hypoM status is associated with the molecular high-risk classifier,22 methylation level remains an independent prognostic factor. Moreover, methylation status does not seem to influence the initial clinical response to therapy since there were no significant differences regarding the glucosteroids and initial chemotherapy responses (chemosensitivity or MRD) between hypoM and hyperM patients. Methylation status could therefore represent a relevant additional prognostic factor for adult T-ALL. Nevertheless, further validation by another independent series is needed. Moreover, it would be interesting to study the prognostic impact of this methylation signature in T-LBL, which displayed similar methylation distortion patterns.
We used the relatively new methodology of methyla- tion specific-multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplifi- cation (MS-MLPA) to evaluate the promoter DNA methy- lation level. MS-MLPA is a powerful and easy-to-perform PCR-based technique and we demonstrated that MS- MLPA could provide an attractive alternative way to assess methylation classification compared to array analy- sis. This approach permits methylation analysis of multi- ple targets in a single experiment and has been successful- ly used to evaluate the diagnostic relevance of different markers in several tumor types including lung,23 rectal,24 breast,25 bladder,26 prostate,27 and adrenocortical cancer.28
A
B
CDE
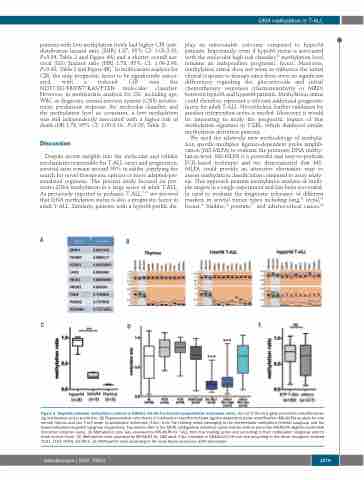
Figure 3. Targeted promoter methylation analysis in GRAALL 03/05 T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias series. (A) List of the nine gene promoters classifier allow- ing methylation status prediction. (B) Representative ratio charts of methylation specific-multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA) analysis for one normal thymus and two T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias (T-ALL) from the training series belonging to the intermediate methylated (interM) subgroup and the hypermethylated (hyperM) subgroup respectively. Top panels refer to the MLPA (undigested) reference panel and the bottom panel the MS-MLPA (digested with HhAI restriction enzyme) panel. (C) Methylation ratio was assessed by MS-MLPA for T-ALL from the training series and according to their methylation subgroup and for three normal thymi. (D) Methylation ratio assessed by MS-MLPA for 168 adult T-ALL included in GRAALL03/05 trial and according to the driver oncogene involved (TLX1, TLX3, HOXA, SIL-TAL1). (E) Methylation ratio according to the early thymic precursor (ETP) phenotype.
haematologica | 2020; 105(6)
1579