Page 269 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 269
Different functions for FXII and PK in sepsis
inhibitor PKSI19 to normal plasma prolonged clot lysis induced by streptokinase (Figure 5B). Complementation of human congenital FXII- or PPK-deficient plasma with acti- vated enzymes (FXIIa or PK) could reverse shortening or prolongation of clot lysis by streptokinase (Figure 5B). Plasminogen content was slightly reduced in FXII-deficient plasma (97±5 mg/mL) comparing to pooled normal plasma (141m8 mg/mL) or PPK deficient plasma (123m28 mg/mL). However, plasmin activity after activation with streptoki- nase was similar in all plasma types (Online Supplementary Figure S2A), providing proof that the streptokinase/plasmin activity is not inhibited due to different donors.
Activation of fibrinolysis results in the release of D-dimer from cross-linked fibrin; thus, we measured the content of D-dimer in the supernatant from human plas- ma clots, which contained S. pyogenes bacteria. Twenty minutes after incubation, D-dimer were detected in sam- ples from clots in FXII-deficient plasma, but not in samples from clots in normal or PPK-deficient plasma (Figure 5C). Thirty minutes after incubation, D-dimer could be detect- ed from clots in normal plasma and FXII-deficient plasma complemented with FXIIa, but still not from clots in PPK- deficient plasma. Forty-five minutes after incubation, D-dimer were detected in the supernatant of PPK-defi- cient plasma, and this time-lag could be reversed by com- plementation with PK (Figure 5C). As expected, in plas- minogen-depleted plasma, no D-dimer were detected within 180 min, but after complementation with plas- minogen D-dimer, release occurred after 30 min. Complete clot lysis by the bacteria could be observed when D-dimer concentration was at the highest level, i.e.
after 20 min in FXII-deficient plasma, after 30 min in nor- mal plasma, and after 45-50 min in PPK-deficient plasma. As clot lysis time and D-dimer production were deceler-
ated in PPK-def. plasma, we investigated whether PK might accelerate plasmin degradation of fibrinogen. Western blot analysis shows that pure fibrinogen is degraded by the streptokinase/plasminogen complex within 5- 10 min, and addition of PPK supports fibrinogen degradation further (Figure 5D and F). Of note, PPK was activated by Ska/plasminogen in the presence of fibrino- gen (Online Supplementary Figure S2C and D). If PPK and FXII were added to fibrinogen it was degraded within 30 min, comparable to plasmin (Figure 5E and G). PPK or FXII alone had marginal effects on fibrinogen degradation, and blocking the proteases by PKSI or CTI inhibited degradation (Online Supplementary Figure S2B). Intriguingly, the degradation pattern of PK cleaved alpha chain of fibrinogen was different, compared to the FXII or the plasmin cleavage pattern (Online Supplementary Figure S2E). We conclude that PPK, activated either by streptok- inase/plasminogen or by FXIIa supports plasmin mediated degradation of fibrinogen.
We also investigated the structure of plasma clots by scanning electron microscopy. Clots derived from PPK- deficient plasma had thinner fibrin strands than clots from normal or FXII-deficient plasma (Figure 5H).
Plasma kallikrein promotes bacterial escape from mouse plasma clots
Streptokinase was shown to specifically activate human plasminogen,20 but S. pyogenes is able to escape from
AB
CD
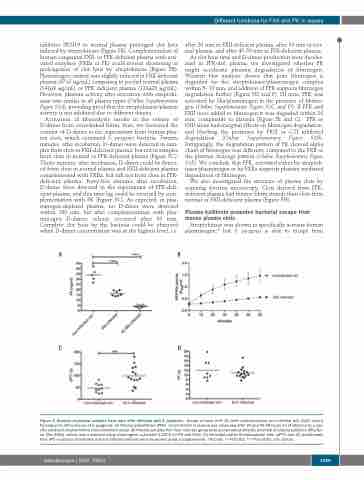
Figure 2. Analysis of plasma samples from mice after infection with S. pyogenes. Groups of mice (n=4-10) were subcutaneously (sc.) infected with 2x107 colony forming units (CFU)/mouse of S. pyogenes. (A) Plasma prekallikrein (PPK) concentration in plasma was measured after 24 and 42-48 hours (h) of infection by a spe- cific sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (B) Plasma samples from four mice per group were pooled and proteolytic potential of plasma kallikrein (PK)/fac- tor XIIa (FXIIa) activity was measured using chromogenic substrate S-2302 for PK and FXIIa. (C) Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and (D) prothrombin time (PT) in plasma of infected and non-infected animals were measured using a coagulometer. *P≤0.05; **P≤0.001; ***P≤0.0001. ctrl: control.
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1429