Page 241 - Haematologica May 2020
P. 241
IL6R-STAT3-ADAR1(P150) interplay in 1q21(amp) MM
Potential therapeutic implications of the IL6R-P150-STAT3 interaction
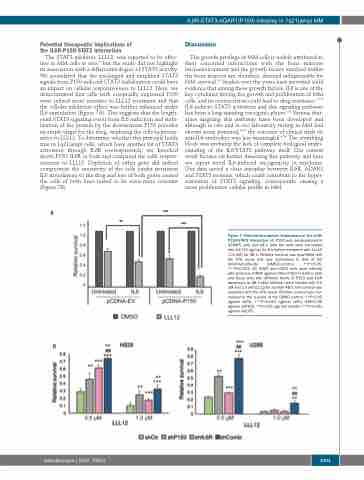
The STAT3 inhibitor, LLL12, was reported to be effec- tive in MM cells in vitro,33 but the study did not highlight its association with a differential degree of STAT3 activity. We postulated that the prolonged and amplified STAT3 signals from P150-induced STAT3 stabilization could have an impact on cellular responsiveness to LLL12. Here, we demonstrated that cells with ectopically expressed P150 were indeed more sensitive to LLL12 treatment and that the cellular inhibition effect was further enhanced under IL6 stimulation (Figure 7A). This suggests that the length- ened STAT3 signaling event from IL6 induction and stabi- lization of the protein by the downstream P150 provides an ample target for the drug, rendering the cells hypersen- sitive to LLL12. To determine whether this principle holds true in 1q21(amp) cells, which have another hit of STAT3 activation through IL6R overexpression, we knocked down P150, IL6R or both and compared the cells’ respon- siveness to LLL12. Depletion of either gene did indeed compromise the sensitivity of the cells (under persistent IL6 stimulation) to the drug and loss of both genes caused the cells of both lines tested to be even more resistant (Figure 7B).
A
Discussion
The growth privilege of MM cells is widely attributed to their concerted interactions with the bone marrow microenvironment and the growth factors enriched within the bone marrow are, therefore, deemed indispensable for MM survival.3,5 Studies over the years have provided solid evidence that among these growth factors, IL6 is one of the key cytokines driving the growth and proliferation of MM cells, and its oversecretion could lead to drug resistance.1,4,13 IL6 induces STAT3 activation and this signaling pathway has been a long-standing oncogenic player.1,33 Various ther- apies targeting this pathway have been developed and although in vitro and in vivo laboratory testing in MM had shown some potential,34-36 the outcome of clinical trials on anti-IL6 antibodies was less meaningful.37,38 The stumbling block was probably the lack of complete biological under- standing of the IL6/STAT3 pathway itself. Our current work focuses on further dissecting this pathway and here we report novel IL6-induced oncogenicity in myeloma. Our data unveil a close interplay between IL6R, ADAR1 and STAT3 proteins, which could contribute to the hyper- activation of STAT3 signaling, consequently causing a more proliferative cellular profile in MM.
Figure 7. Potential therapeutic implications of the IL6R- P150-STAT3 interaction. (A) P150 was overexpressed in OCIMY5 cells and 48 h later the cells were stimulated with IL6 (10 ng/mL) for 8 h before treatment with LLL12 (1.0 mM) for 48 h. Relative survival was quantified with the CTG assay and was normalized to that of the dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)-control. **P<0.05, ***P<0.001. (B) H929 and U266 cells were infected with lentivirus shRNA against either P150 or IL6R or both and these cells with different levels of P150 and IL6R expression at 48 h after infection were treated with 0.5 mM and 1.0 mM LLL12 for another 48 h. Cell survival was assessed with the CTG assay. Relative survival was nor- malized to the survival of the DMSO control. **P<0.05 against shCtr, ***P<0.001 against shCtr, ##P<0.05 against shP150, ^^P<0.05 aga inst shIL6R, ^^^P<0.001 against shIL6R.
B
haematologica | 2020; 105(5)
1401