Page 273 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 273
Inflammation and TTP
Discussion
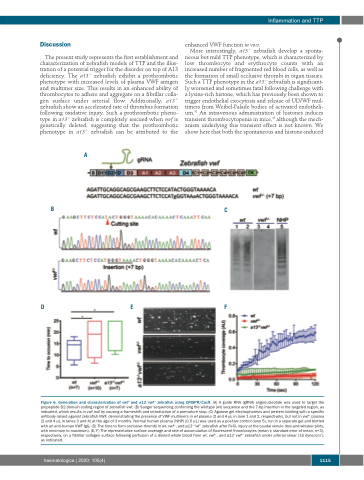
The present study represents the first establishment and characterization of zebrafish models of TTP and the illus- tration of a potential trigger for the disorder on top of A13 deficiency. The a13-/- zebrafish exhibit a prothrombotic phenotype with increased levels of plasma VWF antigen and multimer size. This results in an enhanced ability of thrombocytes to adhere and aggregate on a fibrillar colla- gen surface under arterial flow. Additionally, a13-/- zebrafish show an accelerated rate of thrombus formation following oxidative injury. Such a prothrombotic pheno- type in a13-/- zebrafish is completely rescued when vwf is genetically deleted, suggesting that the prothrombotic phenotype in a13-/- zebrafish can be attributed to the
A
B
DEF
Figure 6. Generation and characterization of vwf-/- and a13-/-vwf-/- zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9. (A) A guide RNA (gRNA) oligonucleotide was used to target the propeptide D2 domain-coding region of zebrafish vwf. (B) Sanger sequencing confirming the wildtype (wt) sequence and the 7-bp insertion in the targeted region, as indicated, which results in vwf null by causing a frameshift and introduction of a premature stop. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis and western blotting with a specific antibody raised against zebrafish VWF, demonstrating the presence of VWF multimers in wt plasma (2 and 4 μL in lane 1 and 2, respectively), but not in vwf-/- plasma (2 and 4 μL in lanes 3 and 4) at the age of 3 months. Normal human plasma (NHP) (0.5 μL) was used as a positive control (lane 5), run in a separate gel and blotted with an anti-human VWF IgG. (D) The time to form occlusive thrombi in wt, vwf-/-, and a13-/-vwf-/- zebrafish after FeCl3 injury at the caudal venule (box-and-whisker plots, with minimum to maximum). (E, F) The representative surface coverage and rate of accumulation of fluorescent thrombocytes (mean ± standard error of mean, n=3), respectively, on a fibrillar collagen surface following perfusion of a diluted whole blood from wt, vwf-/-, and a13-/-vwf-/- zebrafish under arterial shear (15 dyne/cm2), as indicated.
enhanced VWF function in vivo.
More interestingly, a13-/- zebrafish develop a sponta-
neous but mild TTP phenotype, which is characterized by low thrombocyte and erythrocyte counts with an increased number of fragmented red blood cells, as well as the formation of small occlusive thrombi in organ tissues. Such a TTP phenotype in the a13-/- zebrafish is significant- ly worsened and sometimes fatal following challenge with a lysine-rich histone, which has previously been shown to trigger endothelial exocytosis and release of ULVWF mul- timers from Weibel-Palade bodies of activated endotheli- um.42 An intravenous administration of histones induces transient thrombocytopenia in mice,43 although the mech- anism underlying this transient effect is not known. We show here that both the spontaneous and histone-induced
C
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
1115