Page 216 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 216
A. Mikulasova et al.
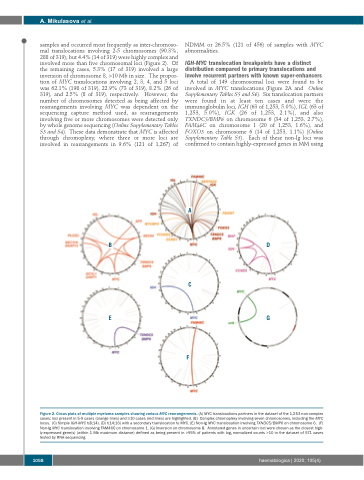
samples and occurred most frequently as inter-chromoso- mal translocations involving 2-5 chromosomes (90.3%, 288 of 319); but 4.4% (14 of 319) were highly complex and involved more than five chromosomal loci (Figure 2). Of the remaining cases, 5.3% (17 of 319) involved a large inversion of chromosome 8, >10 Mb in size. The propor- tion of MYC translocations involving 2, 3, 4, and 5 loci was 62.1% (198 of 319), 22.9% (73 of 319), 8.2% (26 of 319), and 2.5% (8 of 319), respectively. However, the number of chromosomes detected as being affected by rearrangements involving MYC was dependent on the sequencing capture method used, as rearrangements involving five or more chromosomes were detected only by whole genome sequencing (Online Supplementary Tables S3 and S4). These data demonstrate that MYC is affected through chromoplexy, where three or more loci are involved in rearrangements in 9.6% (121 of 1,267) of
NDMM or 26.5% (121 of 456) of samples with MYC abnormalities.
IGH-MYC translocation breakpoints have a distinct distribution compared to primary translocations and involve recurrent partners with known super-enhancers
A total of 149 chromosomal loci were found to be involved in MYC translocations (Figure 2A and Online Supplementary Tables S5 and S6). Six translocation partners were found in at least ten cases and were the immunoglobulin loci, IGH (63 of 1,253, 5.0%), IGL (63 of 1,253, 5.0%), IGK (26 of 1,253, 2.1%), and also TXNDC5/BMP6 on chromosome 6 (34 of 1,253, 2.7%), FAM46C on chromosome 1 (20 of 1,253, 1.6%), and FOXO3 on chromosome 6 (14 of 1,253, 1.1%) (Online Supplementary Table S5). Each of these non-Ig loci was confirmed to contain highly-expressed genes in MM using
A
BD
C
EG
F
Figure 2. Circos plots of multiple myeloma samples showing various MYC rearrangements. (A) MYC translocations partners in the dataset of the 1,253 non-complex cases; loci present in 5-9 cases (orange lines) and ≥10 cases (red lines) are highlighted. (B) Complex chromoplexy involving seven chromosomes, including the MYC locus. (C) Simple IGH-MYC t(8;14). (D) t(14;16) with a secondary translocation to MYC. (E) Non-Ig MYC translocation involving TXNDC5/BMP6 on chromosome 6. (F) Non-Ig MYC translocation involving FAM46C on chromosome 1. (G) Inversion on chromosome 8. Annotated genes in uncertain loci were chosen as the closest high- ly-expressed gene(s) (within 1 Mb maximum distance) defined as being present in >95% of patients with log2 normalized counts >10 in the dataset of 571 cases tested by RNA-sequencing.
1058
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)