Page 215 - Haematologica April 2020
P. 215
MMEJ drives 8q24 rearrangements in myeloma
Results
MYC rearrangements are usually present as inter-chromosomal translocations, co-occur with secondary genetic events, and are associated with shorter survival in non-hyperdiploid cases
We examined a set of 1,267 NDMM patient samples that had undergone either whole genome sequencing, exome sequencing, or targeted sequencing, of which the latter two methods involved capture of 2.3 Mb and 4.5 Mb, respectively, surrounding the MYC locus. Structural abnor- malities involving the region surrounding MYC, including translocations, inversions, tandem-duplications and dele- tions, were detected in 36.0% (456 of 1,267) of NDMM samples. Of these 456, 56.6% (258 of 456) had only a translocation, and 30.0% (137 of 456) had only an intra- chromosomal rearrangement. In 13.4% (61 of 456), both translocation and intra-locus rearrangement were present.
Non-synonymous MYC mutations were rarely detected (0.7%, 9 of 1,264) (Online Supplementary Table S2).
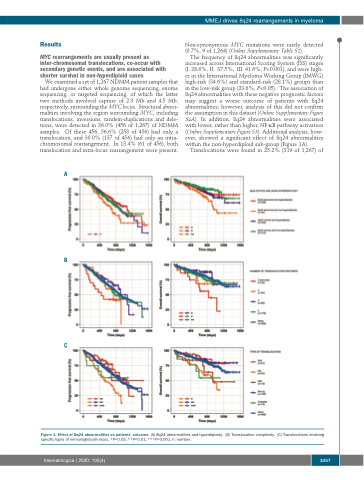
The frequency of 8q24 abnormalities was significantly increased across International Scoring System (ISS) stages (I: 28.6%, II: 37.5%, III: 41.6%; P<0.001), and were high- er in the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) high-risk (34.6%) and standard-risk (28.1%) groups than in the low-risk group (23.6%; P<0.05). The association of 8q24 abnormalities with these negative prognostic factors may suggest a worse outcome of patients with 8q24 abnormalities; however, analysis of this did not confirm the assumption in this dataset (Online Supplementary Figure S4A). In addition, 8q24 abnormalities were associated with lower, rather than higher, NF-κB pathway activation (Online Supplementary Figure S3). Additional analysis, how- ever, showed a significant effect of 8q24 abnormalities within the non-hyperdiploid sub-group (Figure 1A).
Translocations were found in 25.2% (319 of 1,267) of
A
B
C
Figure 1. Effect of 8q24 abnormalities on patients’ outcome. (A) 8q24 abnormalities and hyperdiploidy. (B) Translocation complexity. (C) Translocations involving specific types of immunoglobulin locus. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. n: number.
haematologica | 2020; 105(4)
1057