Page 223 - Haematologica March 2020
P. 223
CDCA7 promotes lymphoma invasion
CDCA7 may regulate the expression or the activity of other enzymes involved in basement membrane degrada- tion, such as heparanases and sulfatases.41,42
The histological barriers confronting metastasizing cells vary in ECM composition, organization, and biophysical characteristics. Cells might therefore use different means to negotiate these diverse physical barriers. While, as mentioned above, normal lymphocytes are facilitated in their crossing of basement membrane by MMP,38 their migration within three-dimensional collagen matrices was insensitive to a protease inhibitor cocktail targeting MMP, serine proteases, cysteine proteases, and cathepsins.12 In contrast, the invasive behavior of epithelial cancer cells was impaired by pharmacological inhibition of proteas-
A
es.13 These results suggest that instead of clearing a path for tissue invasion, normal lymphocytes use protease- independent mechanisms to slither through interstices in the stromal ECM. Similarly, ECM degradation is not required for lymphoma cell migration.43
The protease-independent fashion of negotiating physi- cal barriers involves the coordinated adoption of an amoe- boid type of migration and the use of actomyosin-based mechanical forces to physically displace matrix fibrils.6 Similar to the mesenchymal type of movement adopted by epithelial cells, amoeboid migration requires dynamic assembly/disassembly of the actomyosin network.15 However, while mesenchymal migration relies strongly on coordinated cell adhesion to the ECM in the leading
B
D
E
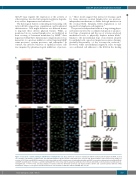
Figure 6. Increased α-actinin staining in CDCA7-silenced lymphoma cells. BL-2 and Toledo cells were transduced with the indicated short hairpin (sh) RNA, seeded on coverslips coated with 2 mg fibronectin, and stimulated with 10 ng/mL stromal cell-derived factor 1 for 15 min. Representative confocal microscopy images (1 section) of (A) Toledo and (B) BL-2 transduced cells stained with an anti-α-actinin monocolonal antibody (mAb) and DAPI or an anti-α-actinin polyclonal antibody (Poly) and DAPI. Quantification of relative α-actinin staining with the monoclonal and the polyclonal antibodies in (C) Toledo and (D) BL-2 cells transduced as indicated. ns, non-significant; ****P<0.0001 (one-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post-test). (E) Representative CDCA7 and α-actinin (probed with the mAb) immunoblot analysis of cell lysates from BL-2 and Toledo cells transduced with the indicated shRNA. Bar, 10 mm.
C
haematologica | 2020; 105(3)
737