Page 129 - 2019_11 Resto del Mondo-web
P. 129
CUDC-907 monotherapy in AML
CUDC-907 treatment induces DNA damage in acute myeloid leukemia cells but spares normal human bone marrow mononuclear cells
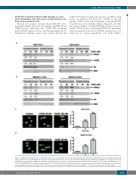
Western blot analysis revealed that CUDC-907 treat- ment substantially increased chromatin-bound RPA32 and γH2AX levels, indicating that CUDC-907 treatment induced DNA replication stress and damage (Figure 6A, B). Furthermore, alkaline comet assay results showed that
A
CUDC-907 induced significant increases in DNA strand breaks, as indicated by increased %DNA in the tail (greater %DNA in the tail corresponds to increased DNA strand breaks), for both AML cell lines (Figure 6C, D). The pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK did not have an effect on the %DNA in the tail following CUDC-907 treatment, demonstrating that the increased DNA damage was not a reflection of caspase-dependent cell death (Online
B
C
D
Figure 6. CUDC-907 treatment induces DNA replication stress and damage in acute myeloid leukemia cells but not in normal human bone marrow mononuclear cells. (A, B) U937 (A) and MOLM-13 (B) cells were treated with CUDC-907 for 16 or 24 h. Chromatin-bound and soluble RPA32 and γH2AX were analyzed by western blotting and probed with the indicated antibodies. Densitometry measurements, normalized to histone H4 and then compared to the control, are indicated. (C, D) U937 (C) and MOLM-13 (D) cells were treated with CUDC-907 for 16 h and then subjected to alkaline comet assay analysis. Representative images are shown. Data are presented as mean percent DNA in the tail from three replicate gels ± the standard error of mean (SEM). ***P<0.001. (continued on the next page)
haematologica | 2019; 104(11)
2235