Page 179 - 2019_01-Haematologica-web
P. 179
Prognostic markers in autoimmune TTP
Birmingham (n=13, 17.8%), and Tuscaloosa (n=9, 12.3%). The remaining patients were from other locations in the state of Alabama with a small number coming from other states including Mississippi, Georgia, New York, Oregon, and Ohio (Figure 1A). Thus, this cohort represents a
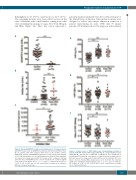
Figure 2. Plasma ADAMTS13 activity and autoantibodies in 73 unique patients with iTTP. Plasma levels of ADAMTS13 activity (A) and functional inhibitor titers (B) in patients with iTTP compared with those in the healthy controls. Additionally, plasma anti-ADAMTS13 IgG levels in iTTP patients with negative (<0.4 U/mL) and positive (>=0.4 U/mL) inhibitors are shown (C). Each individual dot represents a single patient with the median ± 95% confidence intervals (solid red lines). Mann-Whitney was used to determine the statistical signifi- cance between two groups. Here *, **, ***, and **** indicate the P values of <0.05, <0.001, 0.0005, and <0.0001, respectively; n.s. stands for no statistical difference between two groups.
patient population primarily from the southeastern part of the United States of America. Since inclusion criteria were designed to collect only unique admission events for a patient experiencing an acute iTTP, only 73 unique patients of 142 admissions for the diagnosis and treatment
Figure 3. Plasma levels of VWF antigen and collagen-binding activitity in patients with iTTP. Plasma VWF antigen (VWF-Ag) (A), collagen-binding activity (VWF-CBA) (B), and the ratio of VWF-CBA to VWF-Ag (C) were determined in patients with iTTP (initial vs. exacerbated or relapsed) and the healthy controls. Each dot represents a single patient and solid lines are the median ± 95% con- fidence intervals. Kruskal-Willis analysis was used to determine the statistical significance among three different groups. Here *, **, ***, and **** indicate the P values of <0.05, <0.001, 0.0005, and <0.0001, respectively; n.s. stands for no statistical difference.
A
B
C
A
B
C
haematologica | 2019; 104(1)
169