Page 220 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 220
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
for 48 h in the presence of rIL-2 (Online Supplementary Figure S1F). We found that both inhibitors were able to in- hibit mostly (UO126) or completely (GDC-0941) the secre- tion of interferon-γ after 48 h of culture (Online Supplementary Table 1). Taken together, these results pro- vide evidence that deregulated JAK3 and its correspond- ing downstream substrates are involved in the excessive secretion of interferon-γ in NKTCL.
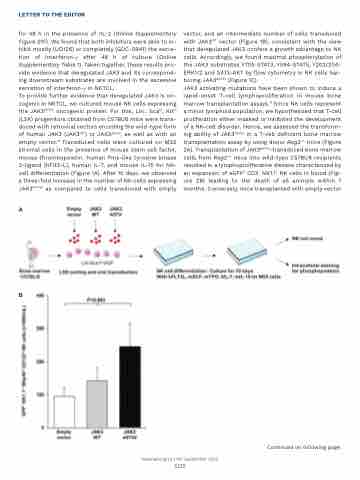
To provide further evidence that deregulated JAK3 is on- cogenic in NKTCL, we cultured mouse NK cells expressing the JAK3A573V oncogenic protein. For this, Lin-, Scahi, Kithi (LSK) progenitors obtained from C57Bl/6 mice were trans- duced with retroviral vectors encoding the wild-type form of human JAK3 (JAK3WT) or JAK3A573V, as well as with an empty vector.8 Transduced cells were cultured on MS5 stromal cells in the presence of mouse stem cell factor, mouse thrombopoietin, human Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3-ligand (hFlt3-L), human IL-7, and mouse IL-15 for NK- cell differentiation (Figure 1A). After 10 days, we observed a three-fold increase in the number of NK cells expressing JAK3A573V as compared to cells transduced with empty
vector, and an intermediate number of cells transduced with JAK3WT vector (Figure 1B), consistent with the view that deregulated JAK3 confers a growth advantage to NK cells. Accordingly, we found maximal phosphorylation of the JAK3 substrates Y705-STAT3, Y594-STAT5, Y202/204- ERK1/2 and S473-AKT by flow cytometry in NK cells har- boring JAK3A573V (Figure 1C).
JAK3 activating mutations have been shown to induce a rapid-onset T-cell lymphoproliferation in mouse bone marrow transplantation assays.9 Since NK cells represent a minor lymphoid population, we hypothesized that T-cell proliferation either masked or inhibited the development of a NK-cell disorder. Hence, we assessed the transform- ing ability of JAK3A573V in a T-cell deficient bone marrow transplantation assay by using donor Rag2-/- mice (Figure 2A). Transplantation of JAK3A573V-transduced bone marrow cells from Rag2-/- mice into wild-type C57Bl/6 recipients resulted in a lymphoproliferative disease characterized by an expansion of eGFP+ CD3- NK1.1+ NK cells in blood (Fig- ure 2B) leading to the death of all animals within 7 months. Conversely, mice transplanted with empty vector
A
B
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2219
Continued on following page.