Page 212 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 212
ARTICLE - Effects of specific inhibition of platelet MRP4 R. Wolf et al.
A
B
CD
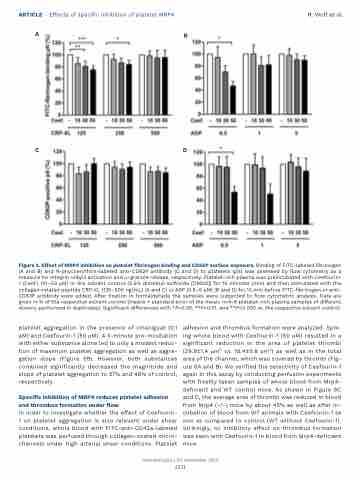
Figure 3. Effect of MRP4 inhibition on platelet fibrinogen binding and CD62P surface exposure. Binding of FITC-labeled fibrinogen (A and B) and R-phycoerythrin-labeled anti-CD62P antibody (C and D) to platelets (plt) was assessed by flow cytometry as a measure for integrin aIIbb3 activation and a-granule release, respectively. Platelet-rich plasma was preincubated with Ceefourin- 1 (Ceef.) (10–50 mM) or the solvent control (0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]) for 15 minutes (min) and then stimulated with the collagen-related peptide CRP-XL (125–500 ng/mL) (A and C) or ADP (0.5–5 mM) (B and D) for 10 min before FITC-fibrinogen or anti- CD63P antibody were added. After fixation in formaldehyde the samples were subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Data are given in % of the respective solvent control (means + standard error of the mean, n=4-6 platelet-rich plasma samples of different donors, performed in duplicates). Significant differences with *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and **P<0.005 vs. the respective solvent control.
platelet aggregation in the presence of cinaciguat (0.1 mM) and Ceefourin-1 (50 mM). A 3-minute pre-incubation with either substance alone led to only a modest reduc- tion of maximum platelet aggregation as well as aggre- gation slope (Figure 5B). However, both substances combined significantly decreased the magnitude and slope of platelet aggregation to 37% and 46% of control, respectively.
Specific inhibition of MRP4 reduces platelet adhesion and thrombus formation under flow
In order to investigate whether the effect of Ceefourin- 1 on platelet aggregation is also relevant under shear conditions, whole blood with FITC-anti-CD42a-labeled platelets was perfused through collagen-coated micro- channels under high arterial shear conditions. Platelet
adhesion and thrombus formation were analyzed. Spik- ing whole blood with Ceefourin-1 (50 mM) resulted in a significant reduction in the area of platelet thrombi (29.9±1.4 mm2 vs. 18.4±0.8 mm2) as well as in the total area of the channel, which was covered by thrombi (Fig- ure 6A and B). We verified the selectivity of Ceefourin-1 again in this assay by conducting perfusion experiments with freshly taken samples of whole blood from Mrp4- deficient and WT control mice. As shown in Figure 6C and D, the average area of thrombi was reduced in blood from Mrp4 (-/-) mice by about 45% as well as after in- cubation of blood from WT animals with Ceefourin-1 ex vivo as compared to control (WT without Ceefourin-1). Strikingly, no inhibitory effect on thrombus formation was seen with Ceefourin-1 in blood from Mrp4-deficient mice.
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2211