Page 210 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 210
ARTICLE - Effects of specific inhibition of platelet MRP4
R. Wolf et al.
A
B
C
In addition, we evaluated the effect of Ceefourin-1 on pla- telet viability using an assay based on the intracellular cal- cein accumulation as described in the Online Supplementary Appendix. Ceefourin-1 in concentrations of up to 50 mM had no significant effect on platelet viability compared to the solvent control (Online Supplementary Figure S4).
Platelet fibrinogen binding and calcium influx is inhibited by Ceefourin-1
The impact of Ceefourin-1 on different sub-aspects of platelet activation, like integrin aIIbb3 activation and a- granule release were assessed by flow cytometric ana- lyses of fluorescence-labeled fibrinogen and anti-CD62P antibody binding. Fibrinogen binding was significantly re- duced by Ceefourin-1 (80.9±4.9% and 75.3±4.0% of control with 30 mM and 50 mM Ceefourin-1, respectively) at a sub- maximal concentration of CRP-XL (Figure 3A). ADP-in- duced fibrinogen binding was also markedly abrogated to 47.1±7.3% of control with 50 mM Ceefourin-1 (Figure 3B). Higher concentrations of the agonists led to a less pro- nounced effect of MRP4 inhibition, which disappeared completely at the highest concentrations used. Addi- tionally, we found CD62P surface exposure to be signifi- cantly reduced upon stimulation with ADP but not with CRP-XL (Figure 3C and D).
Since calcium is essential for the change in conformation of integrin aIIbb3, allowing it to bind fibrinogen, we measured the increase of free cytosolic calcium in Fura- 2-loaded human platelets (Figure 4A to C). In order to dis- criminate between calcium influx and mobilization from intracellular stores, platelets were activated in the pres- ence (left panels) or absence (right panels) of external cal- cium. Blocking MRP4 entails a reduction in the area under the fluorescence curve (area under the curve [AUC]) upon stimulation with ADP, resulting predominantly from an im- paired calcium influx (8.0±0.5 vs. 11.4±0.8 R(340/380)*s in calcium-containing medium). The signal in calcium-free medium, reflecting mobilization from intracellular stores, was markedly lower. However, there was also a trend to- wards reduced AUC values after incubation with Cee- fourin-1 for the calcium mobilization, which became statistically significant when the decrease was calculated relative to the respective solvent control of each blood sample donor (separate experiment) (Figure 4C).
Ceefourin-1 enhances VASP phosphorylation and cyclic nucleotide-dependent platelet inhibition
The cyclic nucleotides cGMP and cAMP are important second messengers involved in platelet inhibition, es- pecially by endothelium-derived factors, such as nitric oxide (NO) or prostacyclin (PGI2). Both cGMP and cAMP are able to activate protein kinases (PK), leading to the phosphorylation and inhibition of proteins, which are in- volved in the signaling for platelet activation. In order to
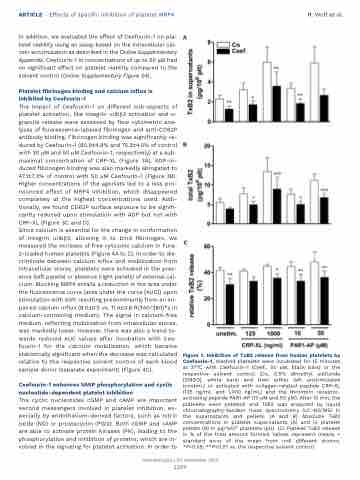
Figure 1. Inhibition of TxB2 release from human platelets by Ceefourin-1. Washed platelets were incubated for 15 minutes at 37°C with Ceefourin-1 (Ceef., 50 mM, black bars) or the respective solvent control (Co, 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO], white bars) and then either left unstimulated (unstim.) or activated with collagen-related peptide CRP-XL (125 ng/mL and 1,000 ng/mL) and the thrombin receptor- activating peptide PAR1-AP (10 mM and 50 mM). After 15 min, the platelets were pelleted and TxB2 was analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) in the supernatants and pellets. (A and B) Absolute TxB2 concentrations in platelet supernatants (A) and in platelet pellets (B) in pg/1x106 platelets (plt). (C) Platelet TxB2 release in % of the total amount formed. Values represent means + standard error of the mean from n=6 different donors. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 vs. the respective solvent control.
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2209