Page 169 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 169
ARTICLE - Immune deficiency during RM after transplantation L. Bouard et al.
AB
C
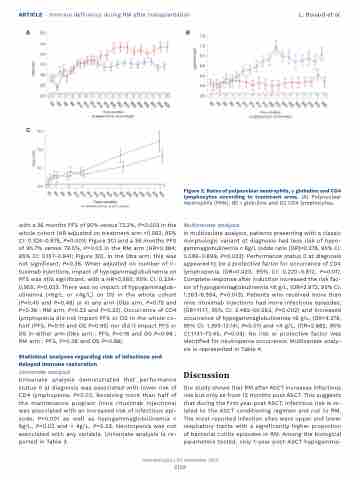
Figure 2. Rates of polynuclear neutrophils, γ globulins and CD4 lymphocytes according to treatment arms. (A) Polynuclear neutrophils (PNN), (B) γ globulins and (C) CD4 lymphocytes.
with a 36 months PFS of 90% versus 73.2%, P=0.003 in the whole cohort (HR adjusted on treatment arm =0.562, 95% CI: 0.324-0.975, P=0.003; Figure 3C) and a 36 months PFS of 95.7% versus 79.5%, P=0.03 in the RM arm (HR=0.384; 95% CI: 0.157-0.941; Figure 3D). In the Obs arm, this was not significant, P=0.36. When adjusted on number of ri- tuximab injections, impact of hypogammaglobulinemia on PFS was still significant, with a HR=0,565; 95% CI: 0,334- 0,955; P=0,033. There was no impact of hypogammaglob- ulinemia (<6g/L or <4g/L) on OS in the whole cohort (P=0.45 and P=0.48) or in any arm (Obs arm, P=0.75 and P=0.38 ; RM arm, P=0.22 and P=0.22). Occurrence of CD4 lymphopenia did not impact PFS or OS in the whole co- hort (PFS, P=0.10 and OS P=0.95) nor did it impact PFS or OS in either arm (Obs arm : PFS, P=0.16 and OS P=0.98 ; RM arm : PFS, P=0.38 and OS P=0.98).
Statistical analyses regarding risk of infections and delayed immune restoration
Univariate analysis
Univariate analysis demonstrated that performance status 0 at diagnosis was associated with lower risk of CD4 lymphopenia, P=0.02. Receiving more than half of the maintenance program (nine rituximab injections) was associated with an increased risk of infectious epi- sode, P<0.001 as well as hypogammaglobulinemia < 6g/L, P=0.02 and < 4g/L, P=0.03. Neutropenia was not associated with any variable. Univariate analysis is re- ported in Table 3.
Multivariate analysis
In multivariate analysis, patients presenting with a classic morphologic variant at diagnosis had less risk of hypo- gammaglobulinemia < 6g/L (odds ratio [OR]=0.278, 95% CI: 0.086-0.899, P=0.033). Performance status 0 at diagnosis appeared to be a protective factor for occurrence of CD4 lymphopenia (OR=0.423, 95% CI: 0.220-0.812, P=0.01). Complete response after induction increased the risk fac- tor of hypogammaglobulinemia <6 g/L, (OR=2.972, 95% CI: 1.263-6.994, P=0.013). Patients who received more than nine rituximab injections had more infectious episodes; (OR=11.17, 95% CI: 2.482-50.263, P=0.002) and increased occurrence of hypogammaglobulinemia <6 g/L; (OR=4.278, 95% CI: 1.393-13.141, P=0.01) and <4 g/L, (OR=2.882, 95% CI:1.131-73.45, P=0.03). No risk or protective factor was identified for neutropenia occurrence. Multivariate analy- sis is represented in Table 4.
Discussion
Our study shows that RM after ASCT increases infectious risk but only as from 12 months post ASCT. This suggests that during the first year post ASCT, infectious risk is re- lated to the ASCT conditioning regimen and not to RM. The most reported infection sites were upper and lower respiratory tracts with a significantly higher proportion of bacterial colitis episodes in RM. Among the biological parameters tested, only 1-year post-ASCT hypogamma-
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2168