Page 140 - Haematologica Vol. 107 - September 2022
P. 140
ARTICLE - A mouse model of humanized type 2B VWD
S. Kanaji et al.
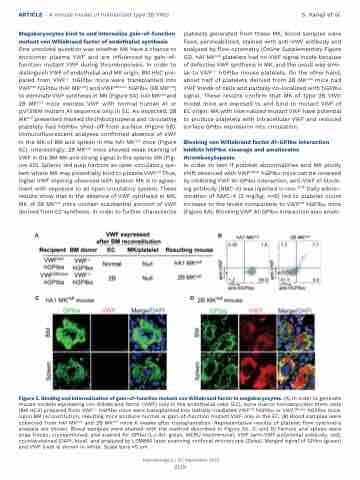
Megakaryocytes bind to and internalize gain-of-function mutant von Willebrand factor of endothelial synthesis One unsolved question was whether MK have a chance to encounter plasma VWF and are influenced by gain-of- function mutant VWF during thrombopoiesis. In order to distinguish VWF of endothelial and MK origin, BM HSC pre- pared from VWF-/- hGPIba mice were transplanted into VWFhA1 hGPIba (hA1 MKnull) and VWF2Bhomo hGPIba (2B MKnull) to eliminate VWF synthesis in MK (Figure 5A). hA1 MKnull and 2B MKnull mice express VWF with normal human A1 or p.V1316M mutant A1 sequence only in EC. As expected, 2B MKnull presented marked thrombocytopenia and circulating platelets had hGPIba shed-off from surface (Figure 5B). Immunofluorescent analyses confirmed absence of VWF in the MK of BM and spleen in the hA1 MKnull mice (Figure 5C). Interestingly, 2B MKnull mice showed weak staining of VWF in the BM MK and strong signal in the splenic MK (Fig- ure 5D). Splenic red pulp harbors an open circulatory sys- tem where MK may potentially bind to plasma VWF.26 Thus, higher VWF staining observed with splenic MK is in agree- ment with exposure to an open circulatory system. These results show that in the absence of VWF synthesis in MK, MK of 2B MKnull mice contain substantial amount of VWF derived from EC synthesis. In order to further characterize
platelets generated from these MK, blood samples were fixed, permeabilized, stained with anti-VWF antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry (Online Supplementary Figure S3). hA1 MKnull platelets had no VWF signal inside because of defective VWF synthesis in MK, and the result was simi- lar to VWF-/- hGPIba mouse platelets. On the other hand, about half of platelets derived from 2B MKnull mice had VWF inside of cells and partially co-localized with hGPIba signal. These results confirm that MK of type 2B VWD model mice are exposed to and bind to mutant VWF of EC origin. MK with internalized mutant VWF have potential to produce platelets with intracellular VWF and reduced surface GPIba expression into circulation.
Blocking von Willebrand factor A1-GPIbα interaction inhibits hGPIbα cleavage and ameliorates thrombocytopenia
In order to test if platelet abnormalities and MK ploidy shift observed with VWF2Bhet hGPIba mice can be reversed by inhibiting VWF A1-GPIba interaction, anti-VWF A1 block- ing antibody (NMC-4) was injected in vivo.27,28 Daily admin- istration of NMC-4 (2 mg/kg, n=6) led to platelet count increase to the levels comparable to VWFhA1 hGPIba mice (Figure 6A). Blocking VWF A1-GPIba interaction also ameli-
AB
CD
Figure 5. Binding and internalization of gain-of-function mutant von Willebrand factor in megakaryocytes. (A) In order to generate mouse models expressing von Willebrand factor (VWF) only in the endothelial cells (EC), bone marror hematopoietic stem cells (BM HCS) prepared from VWF-/- hGPIba mice were transplanted into lethally irradiated VWFhA1 hGPIba or VWF2Bhomo hGPIba mice. Upon BM reconstitution, resulting mice produce normal or gain-of-function mutant VWF only in the EC. (B) Blood samples were collected from hA1 MKnull and 2B MKnull mice 6 weeks after transplantation. Representative results of platelet flow cytometry analysis are shown. Blood samples were stained with the method described in Figure 2A. (C and D) Femurs and spleen were snap frozen, cryosectioned, and stained for GPIba (LJ-Ib1, green, MERU-VasImmune), VWF (anti-VWF polyclonal antibody, red), counterstained (DAPI, blue), and analyzed by LSM880 laser scanning confocal microscope (Zeiss). Merged signal of GPIba (green) and VWF (red) is shown in white. Scale bars =5 mm.
Haematologica | 107 September 2022
2139