Page 212 - Haematologica May 2022
P. 212
Letters to the Editor
B
C
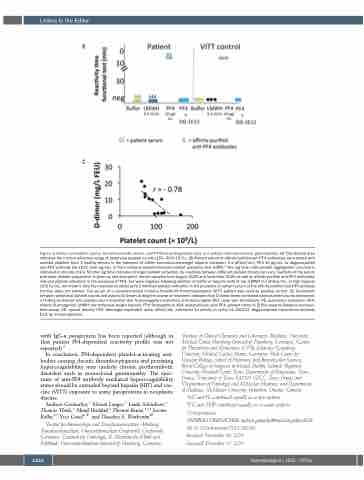
Figure 1: History of platelet counts, thromboembolic events, and PF4-based diagnostic tests in a patient with monoclonal gammopathy. (A) The shaded area indicates the normal reference range of peripheral platelet counts (150–400×109/L). (B) Patient serum or affinity purified anti-PF4 antibodies were tested with washed platelets from 3 healthy donors in the presence of buffer, low-molecular-weight heparin (reviparin, 0.2 aFXaU/mL), PF4 10 μg/mL, or deglycosylated
anti-PF4 antibody DG-1E12 (100 μg/mL) in the functional heparin-induced platelet activation test (HIPA).4 The lag time until platelet aggregation occurred is indicated in minutes (min). Shorter lag time indicates stronger platelet activation. As reactivity between different platelet donors can vary, reactivity of the serum with each platelet preparation is given as one data point. Serum samples from August 2020 and November 2020 as well as affinity purified anti-PF4 antibodies induced platelet activation in the presence of PF4, but were negative following addition of buffer or heparin both at low (LMWH 0.2 aFXaU/mL, or high heparin (100 IU/mL; not shown). Also the monoclonal antibody IV.3 inhibited platelet activation in the presence of patient serum or the affinity purified anti-PF4 antibody fraction (data not shown). The serum of a vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) patient was used as positive control. (C) Correlation between peripheral platelet counts and plasma D-dimers during the course of treatment indicates that D-dimer levels increased when platelet counts decreased, a finding consistent with platelet count reduction due to procoagulant activation and consumption.DVT: deep vein thrombosis; PE: pulmonary embolism; VKA: vitamin K antagonist; LMWH: low-molecular-weight heparin; FPX: fondaparinux; ASA: acetylsalicylic acid; PF4: platelet factor 4; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosor- bent assay; OD: optical density; FEU: fibrinogen equivalent units; aFXaU/mL: anti-factor Xa activity in units/mL; DG-E12: deglycosylated monoclonal antibody E12; Ig: immunoglobulin.
with IgG-k paraprotein has been reported (although in that patient PF4-dependent reactivity profile was not reported).5
In conclusion, PF4-dependent platelet-activating anti- bodies causing chronic thrombocytopenia and persisting hypercoagulability may underly chronic prothrombotic disorders such as monoclonal gammopathy. The spec- trum of anti-PF4 antibody mediated hypercoagulability states should be extended beyond heparin (HIT) and vac- cine (VITT) exposure to some paraproteins in neoplastic disease.
Andreas Greinacher,1* Florian Langer,2* Linda Schönborn,1 Thomas Thiele,1 Munif Haddad,3 Thomas Renné,3,4,5 Jerome Rollin,6,7 Yves Gruel6,7# and Theodore E. Warkentin8#
1Institut für Immunologie und Transfusionsmedizin, Abteilung Transfusionsmedizin, Universitätsmedizin Greifswald, Greifswald, Germany; 2Zentrum für Onkologie, II. Medizinische Klinik und Poliklinik, Universitätsklinikum Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany;
3Institute of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany; 4Center for Thrombosis and Hemostasis (CTH), Johannes Gutenberg University Medical Center, Mainz, Germany; 5Irish Center for Vascular Biology, School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences, Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland, Dublin, Ireland; 6Regional University Hospital Centre Tours, Department of Hemostasis, Tours, France; 7University of Tours, EA7501 GICC, Tours, France and 8Deptarment of Pathology and Molecular Medicine, and Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
*AG and FL contributed equally as co-first authors
#YG and TEW contributed equally as co-senior authors Correspondence:
ANDREAS GREINACHER- andreas.greinacher@med.uni-greifswald.de doi:10.3324/haematol.2021.280366
Received: November 16, 2021.
Accepted: December 17, 2021.
1220
haematologica | 2022; 107(5)