Page 204 - 2022_02-Haematologica-web
P. 204
Letters to the Editor
doses of etoposide or the pesticides fails to induce MLL breaks or to initiate leukemia in NSG-reconstituting human CD34+ HSPC.
We next assessed whether chronic exposure to pesti- cides during embryonic development induces Mll breaks in developing murine HSPC. To do this, CD1 male and female mice were mated and pregnant CD1 females were exposed to etoposide (10 mg/kg/day) or to pesti-
cides (20 mg/kg/day) in drinking water from gestational day 0.5 to day 21 (Figure 3A). No significant differences were found between treatment groups for the number of pups per litter at birth (range, 11–18) or sex distribution (Online Supplementary Figure S3A, B). The mothers and one-half of the litter were euthanized at weaning to ana- lyze the impact of etoposide and pesticides on the Mll locus and on hematopoietic homeostasis, and the
A
B
C
D
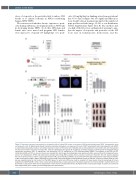
Figure 2. Continuous exposure to permethrin or chlorpyrifos fails to induce MLL breaks or leukemia in NSG-reconstituting human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. (A) Experimental design to determine whether prolonged in vivo exposure of human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) to insecticides induces MLL breaks or can initiate leukemia. In brief, 32 NSG mice were irradiated and cord blood-derived human CD34+ cells were transplanted into the bone marrow 6–8 h later. Four days later, mice were divided into four groups (8 mice/group) to initiate exposure in drinking water to etoposide (ETO, 5 mg/kg/day), permethrin (PER, 10 mg/kg/day), and chlorpyrifos (CPF, 10 mg/kg/day) or 0.1% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO). The presence of the PER and CPF metabolites 3-BPA and TCPy in urine and serum was analyzed 48 h later by gas chromatography-mass spectometry. Mice were sacrificed for interphase fluores- cence in situ hybridization (iFISH) and fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis after 12 weeks of continuous treatment. (B) Left, scheme depicting the human chromosome 11 and the 11q23 region where the MLL probe hybridizes. Middle, representative iFISH image showing human cells with germline MLL or MLL rearrangement (MLLr). Right, percentage of human CD45+ cells harboring MLL breaks detected by iFISH at sacrifice. A minimum of 500 nuclei per sam- ple was analyzed, except in one mouse from the DMSO group, for which only 216 nuclei could be analyzed. (C) Upper panels show the percentage of human engraftment (CD45+HLA-ABC+ cells) in bone marrow and peripheral blood. Lower panels show the relative proportion of immature (CD34+), myeloid (CD33+) and B-cell (CD19+) populations within human engraftment in bone marrow and peripheral blood. (D) Representative macroscopic images of spleens at sacrifice for each experimental group. GC-MS: gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
546
haematologica | 2022; 107(2)