Page 110 - 2022_02-Haematologica-web
P. 110
Y. Liu et al.
As shown in Figure 8A, both shRNA1 and shRNA2 signif- icantly decreased RPS19 mRNA expression, with slightly more efficient knockdown being obtained with shRNA1 than shRNA2, which resembles our previous observations in D/+ and D/D mouse models.15 In order to examine the function of EFS-RPS19, we transduced sorted GFP+ cells and cultured them in erythroid differentiation medium for 48 h after transduction. The PCR results indicated success- ful integration of the vector into human cells, as shown in Online Supplementary Figure S11. It is a well-known phe- nomenon that lentiviral vector-mediated transgene expression is silenced in a fraction of CD34+ cells, and that this fraction increases during differentiation of cells, likely due to changes in chromatin accessibility. As shown in Figure 8B, transgene silencing was evident in a fraction of the Scr-transduced CD34+ cells in which the fraction of GFPhigh shRNA expressing cells decreased from 100% in the sorted cells to around 90% on day 6 and day 10, with a further reduction to around 25% at day 16. However, in the RPS19-deficient groups, the loss of GFPhigh cells was evident from day 6, with an increased fraction of GFPlow
A
and GFP– cells (Online Supplementary Figure S12A-B). By further analysis of cell distribution, significantly decreased outputs of CD71+CD235A– cells on day 6 and CD71– CD235A+ cells on day 10 were observed in GFPhigh popula- tions of RPS19-deficient groups (Online Supplementary Figure S12C, D). The impaired differentiation was rescued by EFS-RPS19, with significantly increased GFPhigh popula- tions (1.6-fold for shRNA1 and 1.8-fold for shRNA2) (Figure 8B) and progenitor populations (CD71+CD235A–) (Online Supplementary Figure S12C) compared to the RPS19-deficient groups on day 6. Particularly, during ter- minal erythropoiesis on day 16, cells in the RPS19-defi- cient groups showed reduced red blood cell production (especially in the shRNA2 group) and few GFPhigh cells (<1%) could be detected (Figure 8C-E). However, EFS- RSP19 vector-treated groups produced more red blood cells and maintained significantly higher GFPhigh popula- tions (~4%) than the RPS19-deficient groups. These results collectively demonstrate that the EFS-RPS19 vector can rescue the impaired erythroid differentiation in human primary RPS19-deficient CD34+ cord blood cells.
BCD
EFG
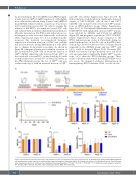
Figure 5. Amelioration of disease phenotype in Rps19-deficient animals transplanted with gene-corrected cells. (A) Scheme of the gene-corrected Rps19-deficient cell transplantation model and plan for examining short-term and long-term therapeutic effects. (B) Survival rate analysis. (C-G) Blood cellularity at 4 and 16 weeks after doxycycline induction (n=14-16, error bars represent the standard deviation, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005 ****P<0.001 by one-way analysis of variance). WT: wild-type; RBC: red blood cells; MCV: mean corpuscular volume; WBC: white blood cells.
452
haematologica | 2022; 107(2)