Page 273 - 2022_01-Haematologica-web
P. 273
Novel GFI1B variant dysregulates oncogenic factors
a dominant negative effect of the exogenous p32 on the p37 endogenous transcription factor in Meg-01 cells (Figure 3C). Of note, similar data were obtained using non-tagged p37 and p32 forms generated to test the effect of a different mutation (c.648+1_648+8delGTGGGCAC) of GFI1B.10
Transcriptional regulation of the CD34 promoter reflects the aberrant expression of CD34 in patients' platelets
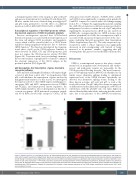
Previous investigations reported that GFI1B-related thrombocytopenia is associated with aberrant expression of the stem cell antigen CD34 in platelets and megakary- ocytes, which could be caused by the loss of CD34 down- regulation during megakaryocytopoiesis due to defective GFI1B function.10 We therefore investigated the transcrip- tional effect of p32 on the CD34 promoter. Similarly to what observed on MEIS, GFI, and GFI1B promoters, p32 does not repress the CD34 promoter activity (P<0.001) (Figure 4A). Consistent with our in vitro findings, immuno- fluorescence analysis of peripheral blood smears confirmed the aberrant expression of the CD34 antigen in the proband’s platelets (II-2) (Figure 4B).
p32 dysregulates the transcription of genes involved in oncogenic pathways
Since myeloid and lymphoid leukemia cells express high- er level of p32 than control cells,26 we hypothesized that p32 could unbalance the transcription of genes involved in malignant transformation. For this reason, we investigated the expression level of other GFI1B targets, including proto- oncogenes GFI1 and MYC, antiapoptotic factors TGFBR3 and BCL2L1, and hematopoietic master regulators, the GATA family members, whose dysregulation is known to occur in oncogenesis. qPCR performed on patients’ periph- eral blood RNA showed that except for GATA2, all the
AB
Figure 4. CD34 expression in c.648+5G>A patients. (A) Transcriptional activity
moter after transient transfection in Meg01 cells. Results are represented by the
as fold change in luciferase activity. Significative variations occur on CD34 transcriptional levels as a significant p32 impaired repression activity is detected in com- parison to p37 active repression (***P<0.001). Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using t-test. (B) Peripheral blood slides of the proband III-2 and healthy volunteers were double-labeled for CD41 (red) and CD34 (green). Platelets were identified by morphology and CD41 expression. Platelets of the proband III-2 showed a clear aberrant expression of the CD34 antigen compared to healthy control (HC). Scale bars correspond to 5 mm.
other genes tested (GFI1, BCL2L1, TGFBR3, MYC, GATA1 and GATA3) were significantly overexpressed in patients II- 2 and III-1 compared to controls with a fold-change ranging from 1.5 to > 3 (Figure 5), suggesting that patients carrying the c.648+5G>A mutation could have an increased risk for malignancies. In order to confirm the role of p37 and p32 in regulating the oncogenic factors, qPCR was also carried out in HEK cells overexpressing the two GFI1B isoforms. As in patients' peripheral blood cells, the overexpression of p32 is associated with an increased expression level of the onco- genes, indicating that p32 up-regulates their transcription (Online Supplementary Figure S1). The only exception is rep- resented by GATA 3, whose expression was significantly decreased in p32-overexpressing cells instead of being increased as in patients’ samples, suggesting that p32 downregulates this gene at least in the HEK cellular model.
Discussion
GFI1B is a transcriptional repressor that plays a funda- mental role in megakaryocyte development and erythro- poiesis9 and pathogenic variants are responsible for the GFI1B-associated bleeding disorder. The novel heterozy- gous GFI1B splicing variant (c.648+5G>A) identified in our family causes alternative splicing leading to unbalanced expression level of the GFI1B isoforms. Specifically, we detected four alternative splicing events, leading to the three known isoforms, p37, p32 and p39, as well as the novel p34 isoform. The p37 and p32 isoforms are expressed at different level in the individuals carrying the c.648+5G>A substitution, with the p32/p37 ratio ten times higher in affected than healthy individuals, indicating that this unbal- ance, due to the presence of the c.648+5G>A mutation,
of p37 (wild-type) and the variant p32 GFI1B isoforms measured on the CD34 pro- ratio of the promoter signal (Firefly) and the control promoter (Renilla) and expressed
haematologica | 2022; 107(1)
265