Page 102 - 2021_12-Haematologica-web
P. 102
J. Li et al.
increased CD69 and decreased PVRIG expression more uni- formly (Figure 3F).
TIGIT and DNAM-1 expression on natural killer cells is modulated by activation
TIGIT and DNAM-1 are NK-cell receptors within the same receptor-ligand axis as PVRIG.9-12 We investigated whether a similar modulation of TIGIT and DNAM-1 occurred following NK-cell activation. In contrast to PVRIG, TIGIT expression was increased after stimulation of NK cells with target cells, cytokines or agonistic antibod- ies (Figure 4A to C), whereas changes in DNAM-1 levels were dependent on the stimulus. DNAM-1 was reduced by interaction with target cells (Figure 4D), but increased
after activation with IL-2 and IL-12 or anti-CD16 (Figure 4E to F). Overall, our results indicated that the expression lev- els for different NK receptors are regulated differently, depending on the stimulus. PVRIG was consistently decreased and TIGIT increased upon NK-cell activation, regardless of the stimulus, and the magnitude of change was correlated with the level of activation. On the other hand, DNAM-1 expression decreased upon target recogni- tion, but was increased by activation via cytokines or ago- nistic antibodies to activating receptors (Figure 4G). The loss of DNAM-1 may result from a form of immune eva- sion, which has previously been described to occur on con- tact with PVR+ tumor cells.22 DNAM-1 increase in response to stimulation via cytokines or activation receptors could
AB
CD
E
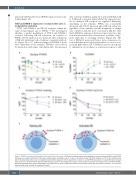
Figure 6. PVRIG is constitutively trafficked to the naural killer cell surface. (A) Poliovirus receptor-related immunoglobulin domain-containing (PVRIG) and (B) CD69 expression on isolated natural killer (NK) cells incubated alone, with K562 cells (1:1 ratio), or with plate-bound anti-CD16 antibody at 37oC for the indicated time points. Representative data (mean ± standard deviation [SD] of duplicates) of two experiments is shown. (C and D) PVRIG expression on isolated NK cells incubated either (C) alone or (D) with plate-bound anti-CD16 antibody at 37oC for the indicated time points, in the presence or absence of monensin (mon) or brefeldin A (BFA). Representative data (mean ± SD of duplicates) of two experiments is shown. Significance determined by multiple t-tests with Holm-Sidak’s correction, *P< 0.05 com- pared with NK alone (A and B) or untreated (C and D).
3122
haematologica | 2021; 106(12)