Page 41 - 2021_10-Haematologica-web
P. 41
Targeting PKC and BET induces differentiation of AML
C
AB
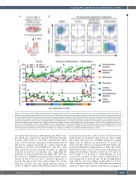
Figure 1. Screening of small natural products identifies compounds that are toxic to acute myeloid leukemia cells or have myeloid differentiation potential. (A) Primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and control cells (CD34+ bone marrow cells) from healthy volunteers were cultured for 2 days on irradiated stromal cells and then treated with 513 natural product compounds at the concentrations of 10 mM and 0.5 mM. Four days later, cells were collected and assayed by flow cytometry to measure their viability (volumetric cell count) and myeloid differentiation (CD11b and CD15 expression). (B) An illustrative example of a hit compound from each of the three categories: toxicity, toxicity and differentiation, and differentiation. (C) Hit compounds were categorized into biological response groups and then on molecular structure. In the ‘differentiation’ category: CD11b >55% (AML-3) and cell number/DMSO ratio >0.5 (all samples). In the ‘toxicity and differentiation’ cate- gory: CD11b >55% (AML-3) and cell number/DMSO ratio <0.5 (any sample). In the ‘toxicity’ category: CD11b <55% (AML-3) and cell number/DMSO ratio <0.5 (any samples). The baseline expression of CD11b for each sample is indicated with a dotted line in a designated color. Data are shown as mean ± standard error of mean from independent experiments, healthy control n=2, AML-1 n=2-3, AML-2 n=1, AML-3 n=2-3. DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide, Ctrl: control.
was specifically efficient in differentiating the AML-3 sam- ple, which was isolated from a patient with chemotherapy- resistant AML (Table 1 and Online Supplementary Figure S1B). A dose-response experiment demonstrated that 10 mM was the optimal concentration to induce myeloid dif- ferentiation (CD11b+ cells: DMSO, 20%, H4, 65%) with May-Grünwald Giemsa staining showing an apparent reduction in nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio, supporting the induction of myeloid differentiation (Figure 2B). The rela- tive decrease to DMSO in cell number at the 10 mM concen- tration on day 4 was not due to increased apoptosis or necrosis throughout the 4-day culture (Figure 2C). In line with this, absolute cell count during long-term culture (4 weeks) of AML-3 together with H4 demonstrated an initial-
ly increased proliferation of the treated cells followed by a sharp decline in cell number after 8 days in culture, while the control cells exposed to DMSO continued to expand (Figure 2D). In addition, the proportion of CD11b+ cells increased with continuous treatment with H4, further sup- porting that H4 induces differentiation of AML cells (Online Supplementary Figure S2A). However, since leukemia-propa- gating cells (leukemia stem cells) are known to be quiescent and thought to be resistant to chemotherapy, we next assessed the potential of H4 to induce differentiation of non-cycling cells, G0-arrested cells, by pre-treating AML-3 cells with the cell cycle inhibitor palbociclib23 for 5 days (Online Supplementary Figure S2B). Even with the continuous addition of palbociclib together with H4, the upregulation
haematologica | 2021; 106(10)
2569