Page 167 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 167
MYB bi-allelic targeting
AB
D
EF
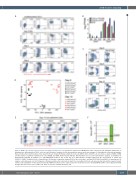
Figure 2. MYB is specifically expressed in the emerging hematopoietic cells. (A) Specific expression of MYB-Venus in the early blood cells during the initial phase of hematopoietic differentiation of SKO1 cells. Here and elsewhere, numbers in flow cytometry plots represent the percentages of cells within the respective quadrants. Representative flow cytometry data of four experiments are shown. (B) Human embryonic stem cells (hESC)-derived CD43+ cells selectively co-express mRNA of MYB and the markers of primitive human blood cells, ITGA2B and GYPA. Differentiated wild-type (WT) H1 hESC were used for transcriptome analysis. (C) Inhibition of Activin/Nodal signaling by addition of 6 mM SB-431542 between day 2 and day 4 of differentiation strongly suppressed the development of CD43+ and CD235a+ /CD41a+ primitive blood cell populations. (D) Principal component analysis (PCA) of the sorted day 6 and day 12 WT, SKO1 and DKO1 cell populations, 31 samples, and entire gene set (19,796 genes). (E) Representative flow cytometry of day 10 live non-adherent blood cells generated by H1 and the isogenic mutant cell lines. (F) Quantitation of data represented in (E). MYB-Venus fluorescence (expressed as the mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) in DKO cells is disproportionally stronger than the fluorescence in SKO cells. Data are mean ± standard deviation, n=4.
C
haematologica | 2021; 106(8)
2195