Page 52 - 2021_07-Haematologica-web
P. 52
J. Hu et al.
derived xenograft (PDX) derived from primary T-ALL sample #1 (Online Supplementary Table S3). Human CD45+ leukemia cells from the spleen were analyzed for glycolysis-related gene expression. Again, MK1775 sup- pressed the expression of several key enzymes involved in the glycolysis pathway (Figure 3H). Taken together, we identify a crucial role of WEE1 in regulation of glu- cose metabolism, in addition to its well-defined function in DNA damage response and cell cycle checkpoint.10 In
this regard, multiple mechanisms account for the anti- tumor efficacy of WEE1 inhibitors.
WEE1 inactivation sensitizes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to glutaminase inhibitors
Glucose and glutamine are two primary nutrients uti- lized by cancer cells for their proliferation and growth. We then surmised that a decrease in glycolysis may render T- ALL cells more addicted to glutaminolysis and glutamine
A
B
C
D
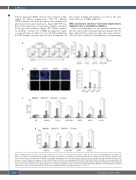
Figure 4. WEE1 inhibition sensitizes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to glutaminolysis inhibition. (A) T-ALL cells were treated with MK1775 (100 nM) in the presence or absence of Glutamine (Gln, 2 mM) for 48 hours (h). Apoptotic cell death was analyzed by Annexin V/PI staining and flow cytometry analysis. (Left) Representative flow cytometry graphs of HPB-ALL cells. (Right) Quantifications of cell death from four T-ALL lines are presented on the right. (B) Immunofluorescence images of cleaved Caspase-3 (c-caspase 3, red) and DAPI (blue) in HPB-ALL cells undergoing DMSO, MK1775(100 nM), CB-839 (100 nM) or dual treatments for 48 h. Scale bar, 50 μm. (Right) Quantifications of fluorescence signals. (C) Apoptotic cell death was analyzed by Annexin V/PI staining in normal bone marrow (BM) and T-ALL cell lines after treatments as in (B). (D) Apoptotic cell death was analyzed in T-ALL cells after treatments with DMSO, MK1775 (100 nM), BPTES (10 mM) and combination for 48 h. Data shown represent the means (± standard deviation) of biological triplicates. **P<0.01.
1822
haematologica | 2021; 106(7)