Page 149 - 2021_07-Haematologica-web
P. 149
Hematopoietic JAK 2V617F in aortic aneurysms
AB
C
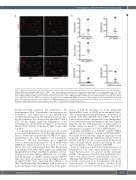
Figure 6. Matrix metalloproteinases are upregulated in bone marrow-derived macrophages with JAK2 V617F expression. (A) Mononuclear cells isolated from bone- marrow (BM) cells of wild-type (WT) mice or JAK2V617F mice were cultured in the presence of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor for 6 days. Representative immunofluorescence images of the cells stained with anti-CD68 (red) antibody and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 100 mm. (B) Relative mRNA expression levels of Mmp2, Mmp9, and Mmp13 in the cultured mononuclear cells (n=7 each). (C) Mmp2 and Mmp9 mRNA expressions with and without ruxolitinib pretreatment at 250 nM for 24 hours in the JAK2V617F mononuclear cells (n=4 each). Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) was used for control. Actb was used for normalization. The average value for the cultured mononuclear cells from WT mice or DMSO group was set to 1. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05 vs. the WT group or DMSO group by the unpaired Student’s t-test. JAK2V617F: JAK2 V617F-expressing transgenic mice.
duction and MMP activation, and contributes to the development of AAA.46 Recruitments of macrophages and neutrophils, and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines may characterize the degenerative process dur- ing AA formation. We observed that the JAK2V617F-BMT mice did not display significant enlargement of the ascending aorta, and therefore it remains to be elucidated whether TAA develops in this model and/or some other condition.
It is known that matrix metalloproteases are closely involved in the pathogenesis of AA through elastin degra- dation.47 Studies have reported that the JAK-STAT signal- ing pathway is one of the regulators of matrix metallo- proteases,48,49 and that macrophages are a significant source of matrix metalloproteinases.47,50 Both MMP-9 and MMP-2 are required and work in concert to produce AAA.36 We have demonstrated here that BM-derived macrophages with JAK2 V617F expression significantly upregulate Mmp2, Mmp9, and Mmp13. Likewise, substan- tially promoted macrophage infiltration was accompa- nied by increases in MMP-2 activity and pro MMP-9 expression in the abdominal aorta in the Ang II-stimulat- ed JAK2V617F-BMT mice, suggesting that infiltration of JAK2 V617F-expressing macrophages with activation of matrix metalloproteinases plays causal roles in the patho-
genesis of AAA. In agreement, we found significantly higher mRNA levels of MMP9 in the peripheral leuko- cytes, containing macrophage-progenitor monocytes, of patients with JAK2 V617F-positive MPN compared to control subjects. MMP-9 plasma levels were independent- ly associated with aortic wall thickness and aortic luminal diameter, but not with parameters of atherosclerosis.31 Further studies are needed to clarify the MMP-related mechanism for progression to AA in MPN patients.
Currently, ruxolitinib is a clinically available JAK1/2 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with PMF and PV.51 Ruxolitinib has been shown to improve long-term survival in patients with PMF and reduced thrombotic events in patients with PV.52-54 Given our observations in the present study, ruxolitinib may be useful for preventing the onset and development of AAA in patients with MPN.
It has recently been reported that clonal expansion of hematopoietic cells with somatic mutations, termed as clonal hematopoiesis, is common in the seemingly healthy older general population, and significantly asso- ciated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.55,56 Although JAK2 V617F has been identified as one of the recurrent somatic mutations in individuals with clonal hematopoiesis, it remains unclear whether clonal hematopoiesis is involved in AA in addition to stenotic
haematologica | 2021; 106(7)
1919