Page 145 - 2021_07-Haematologica-web
P. 145
Hematopoietic JAK 2V617F in aortic aneurysms
A
B
CD
E
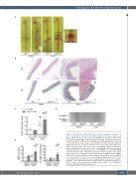
Figure 2. Hematopoietic JAK2 V617F induces elastin degradation and rupture of aortic aneurysm accompanied by matrix metalloproteinase activation. (A) Representative images of the aorta from the WT-BMT mice and JAK2V617F-BMT mice 4 weeks after saline or Ang II or infusion. Scale bars, 5 mm. The boxed area from the Ang II-infused JAK2V617F-BMT mice was highlighted at higher magnification. Scale bar, 2.5 mm. (B) Representative images of hematoxylin-eosin (HE)- and Elastica-Masson (EM)-stained sections. ‘T’ indicates thrombus in the aorta. Black arrow indicates the rupture site of the aorta. Scale bars, 50 mm. (C) Quantitative analysis of degradation grade in EM-stained sections (n=3–5). (D) A typical image of gelatin zymography using homogenates from abdominal aortas of the WT-BMT mice and JAK2V617F-BMT mice 4 weeks after saline or Ang II infusion. (E) Densitometric analysis of the gelatin zymography (n=5–6). The sum of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and pro MMP-2 bands was evaluated as MMP-2 activity. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05 vs. the corresponding saline-infused mice and †P<0.05 vs. the Ang II-infused WT-BMT mice by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc analysis. WT, ApoE−/−: mice transplanted with bone marrow (BM) cells from wild-type (WT) mice; JAK2V617F, ApoE−/−: mice transplanted with BM cells from JAK2V617F mice; BMT: bone- marrow transplantation; Ang II: angiotensin II.
haematologica | 2021; 106(7)
1915