Page 138 - 2021_06-Haematologica-web
P. 138
A.B. Arroyo et al.
A
B
C
D
F
E
G
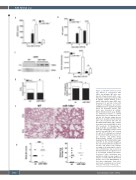
Figure 2. miR-146a deficiency medi- ates NETosis in endotoxemia. miR- 146a-/- and wild-type (WT) mice were injected intraperitoneally with a sub- lethal dose of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 mg/kg). Plasma markers of neu- trophil extracellular traps (NET) were measured 4 h and 24 h after LPS treatment (n=9/group). (A) Cell-free (cf)DNA levels were quantified by Sytox Green. (B) Neutrophil elastase (NE) levels were measured by enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (C) Citrilluniated histone 3 (CitH3) plasma levels were analyzed by west- ern blot. (D) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were quantified by fluorometry 24 h after treatment with LPS. (E) Thrombin-antithrombin (TAT) complex levels were detected by ELISA 4 h after LPS treatment. (F) Morphology of lungs from WT and miR-146a-/- mice after LPS stimulation. Lung sections from WT and miR-146a-/- mice treated 4 h with LPS (1 mg/kg) were stained for reticulin (n=9/group) to observe tis- sue structure and global injury. Representative images of reticulin staining from WT and miR-146a-/- lungs after LPS at 20x and 40x magnifica- tion. (G) Semi-quantitative analysis for reticulin and global lung damage according to the pathologist’s criteria. One section/mouse was scored in a blinded fashion into four grades from 0 to 3 (0=normal, 1=mild, 2=moderate, 3=severe). P-value calculations were performed using one-way analysis of variance on ranks with the Bonferroni post-hoc test or the Mann-Whitney U test, where appropriate. Data repre- sent mean ± standard error of mean, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
1640
haematologica | 2021; 106(6)